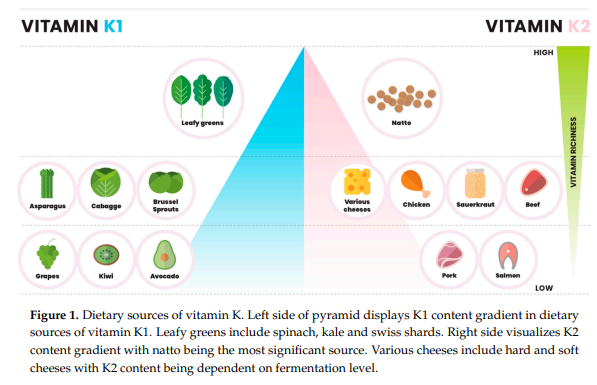
The vitamin K family is comprised of multiple similarly structured fat-soluble molecules containing a 2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone ring structure called menadione. There are three main structures of vitamin K:
- Natural occurring:
- Phylloquinone (K1)
- The predominant form of vitamin K present in the diet.
- Predominantly found in green vegetables and plant chlorophylls.
- Used to treat patients with vitamin K deficiency or to reverse vitamin K antagonists.
- Menaquinones (K2)
- Further subdivided into:
- Short-chain (e.g., menaquinone-4; MK-4)
- Long-chain (e.g.,, MK-7, MK-8, and MK-9)
- Synthesized by bacteria.
- Primarily found in food where bacteria are part of the production process.
- Further subdivided into:
- Phylloquinone (K1)
- Synthetic origin:
- Menadione (K3)
- Converted into K2 in liver.
- Harmful effects shown in humans, therefore not used therapeutically.
Both vitamin K1 and K2 can function as cofactors in the carboxylation process of vitamin K-dependent proteins.
Learn more here.
Related FAQs: