| White blood cell, neutrophil | Toxic granulation |
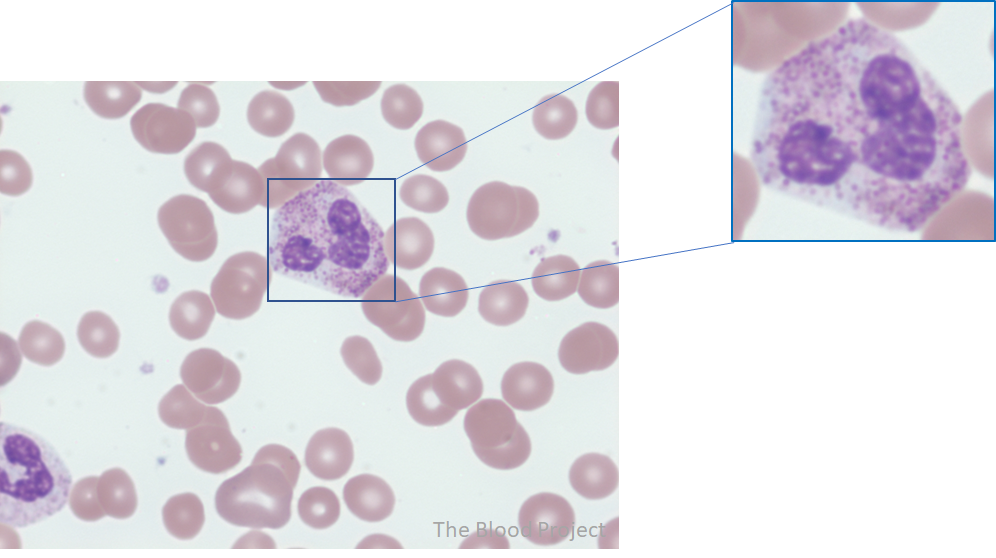
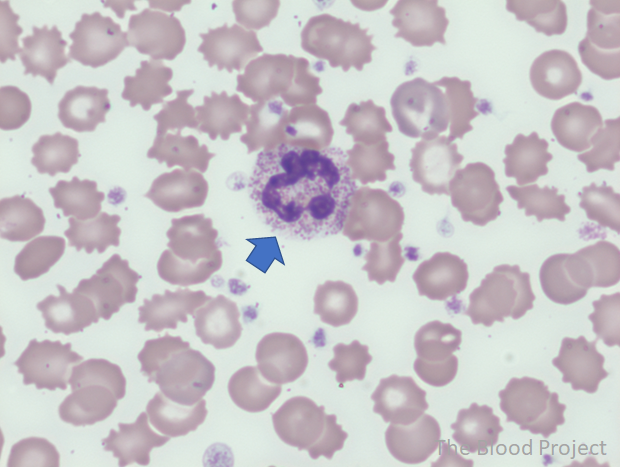
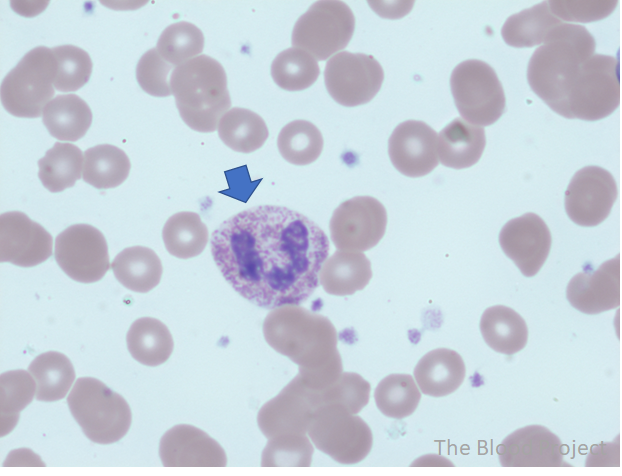
| Definition | Toxic granulation is the presence of large purple or dark blue cytoplasmic granules (primary granules) in neutrophils, bands, and metamyelocytes. The granules are slightly larger, more numerous and have an increased staining density compared to normal neutrophil granules. |
| Conditions associated with toxic granulation | Seen in conditions associated with increase cytokine release such as infection, burns, trauma, and G-CSF. |
| Mechanism | Toxic changes result from the action of cytokines released in response to infection, burns, trauma, and G-CSF (granulocyte colony stimulating factor) and indicate a shortened maturation time and activation of postmitotic neutrophil precursors owing to decreased transit time in bone marrow. |
| Other findings to look for | Often seen with toxic vacuolation, Dohle bodies. Together these three findings are referred to as toxic changes. |
| Source/author | William Aird |
| Reviewed and edited by | Parul Bhargava |