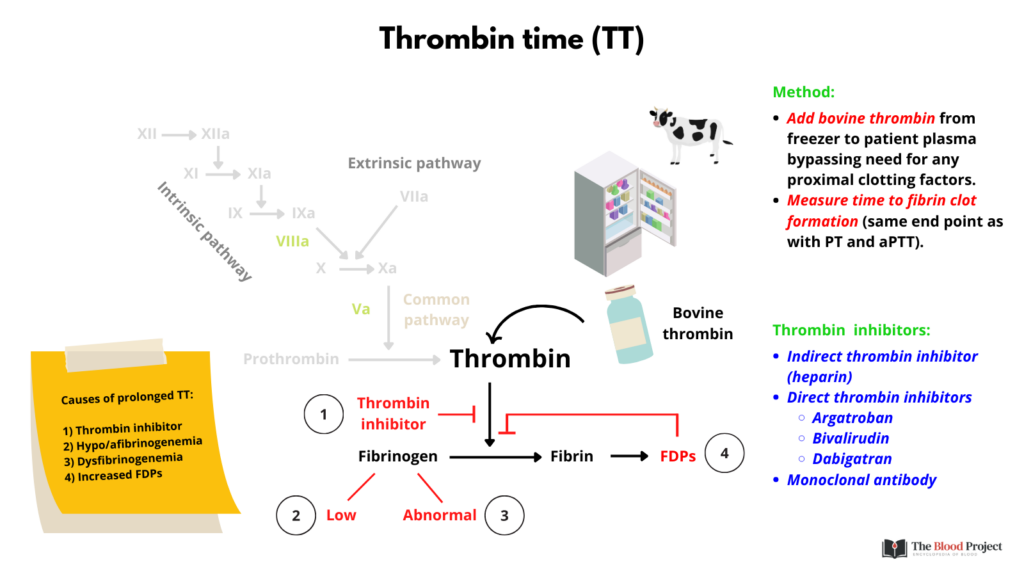
Thrombin time (TT) is a blood test used to assess the clotting ability of blood. Specifically, it measures how long it takes for blood to clot after the addition of thrombin, an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the clotting process.
Here’s a bit more detail on what the test involves and why it’s important:
- Purpose: Thrombin time is used to evaluate the final phase of the coagulation cascade. It’s particularly useful for assessing the presence of certain inhibitors or abnormalities that can affect fibrin formation.
- Process: A sample of blood is mixed with thrombi (thereby bypassing all steps upstream from fibrinogen), and the time it takes for the blood to form a clot is measured. Normally, the blood should clot relatively quickly, but if the thrombin time is prolonged, it can indicate problems with fibrinogen (a protein involved in clot formation) or the presence of inhibitors that interfere with clotting.
- Clinical Use: TT is often used in conjunction with other tests, such as prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), to diagnose and monitor bleeding disorders, liver disease, or the effects of anticoagulant medications.
In summary, thrombin time is a specific test that helps to evaluate the function of the blood clotting system, focusing on the final steps of clot formation.
Click here for larger image.
