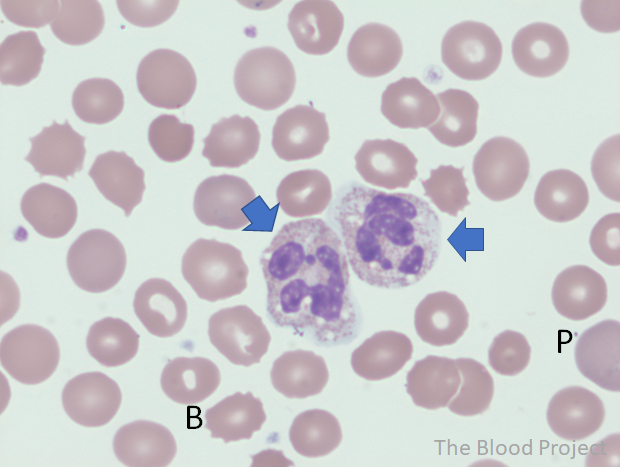
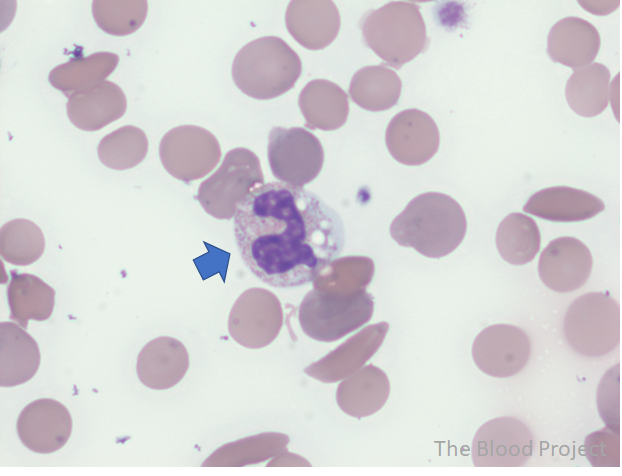
| White blood cell, inclusion | Neutrophil vacuole |
| Definition | Round clear space within the cytoplasm of neutrophils |
| Ddx | EDTA storage may produce degenerative vacuolization; vacuoles typically few in number and not associated with toxic granulation or Döhle bodies. |
| Conditions associated with the inclusion | Seen in conditions associated with increase cytokine release such as infection, burns, trauma, and G-CSF. |
| Mechanism of formation | Arise from phagocytic activity, which is stimulated by the release of cytokines in response to inflammation or tissue injury. |
| Other findings to look for | Vacuoles alone do not constitute toxic change, but when seen in association with toxic granulation and/or Döhle bodies are a feature of toxic change. |
| Source/author | William Aird |
| Reviewed and reviewed by | Parul Bhargava |