| Parameter | Properties |
|---|---|
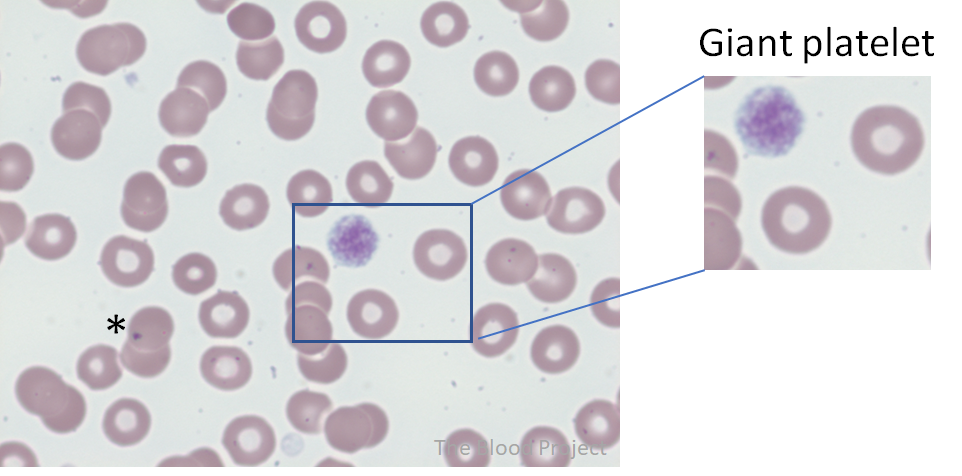
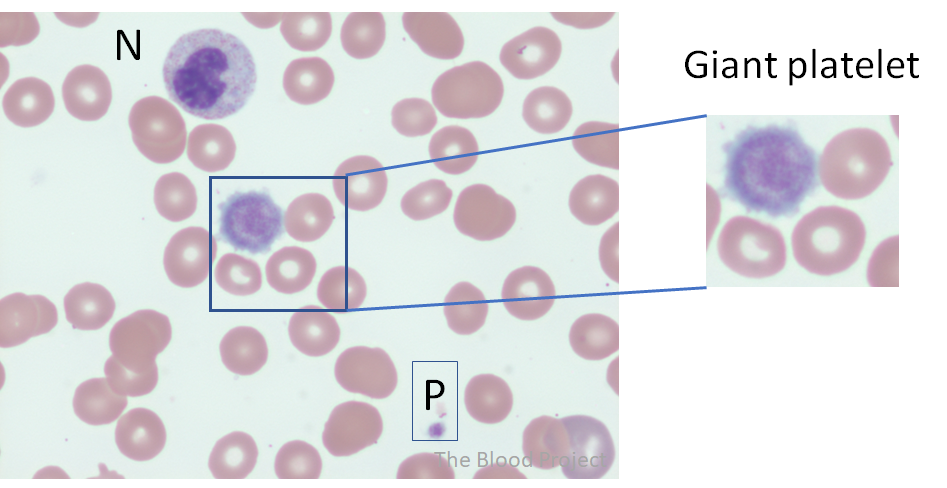
| Platelet | Giant platelet |
| Definition | Most platelets are 1.5-3 μm in diameter. Small platelets are less than 1.5 μm in diameter. Large platelets usually range from 4 to 7 μm. Giant platelets are larger than 7 μm and usually 10-20 μm in diameter. Platelets that are larger than the average normocytic red cell in the field qualify as giant platelets. |
| Conditions associated with the cell type | Seen in many different reactive, neoplastic, and inherited conditions including myeloproliferative and myelodysplastic disorders, autoimmune thrombocytopenia, in association with severe leukemoid reactions, and in a subset of inherited thrombocytopenia such as May-Hegglin anomaly and Bernard-Soulier syndrome. |
| Source/author | William Aird |
| Reviewed and edited by | Parul Bhargava |
| References | Color Atlas of Hematology, CAP1 |
