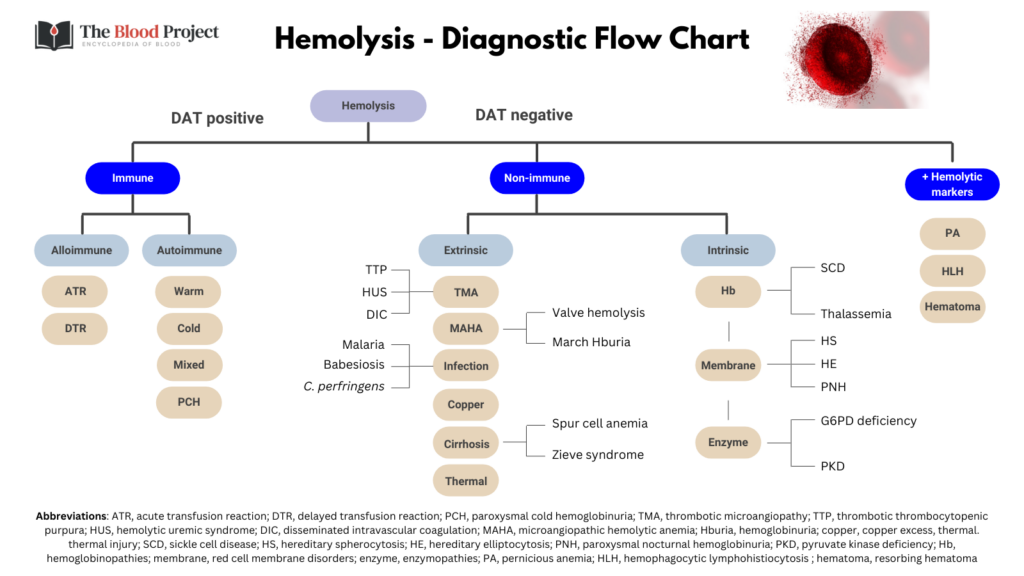
Hemolytic Anemias
Prev
1 / 0 Next
Prev
1 / 0 Next
Hemolytic anemia
Definition
Hb < 12 g/dL (F) or < 13 g/dL (M) typically associated with elevated reticulocyte count and positive hemolytic markers, including:
- Increased LDH
- Increased indirect bilirubin
- Increased AST
- Decreased haptoglobin
Differential diagnosis
- Immune:
- Autoimmune:
- Warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia
- Cold autoimmune hemolytic anemia (cold agglutinin disease)
- Alloimmune:
- Immediate transfusion reaction
- Delayed transfusion reaction
- Autoimmune:
- Non-immune:
- Intracorpuscular:
- Hemoglobinopathy:
- Sickle cell disease
- Thalassemia
- Membranopathy:
- Hereditary spherocytosis
- Hereditary elliptocytosis
- Enzymopathy:
- G6PD deficiency
- Pyruvate kinase deficiency
- Hemoglobinopathy:
- Extracorpuscular:
- Thrombotic microangiopathy
- Valve hemolysis
- March hemoglobinuria
- Spur cell anemia
- Zieve syndrome
- Wilson disease
- Infection
- Babesiosis
- Malaria
- C. perfringens
- Thermal injury
- Intracorpuscular:
- Other conditions associated with positive hemolytic markers:
- Resorbing hematoma
- HLH
- Pernicious anemia
Peripheral smear findings
| Condition | Findings |
|---|---|
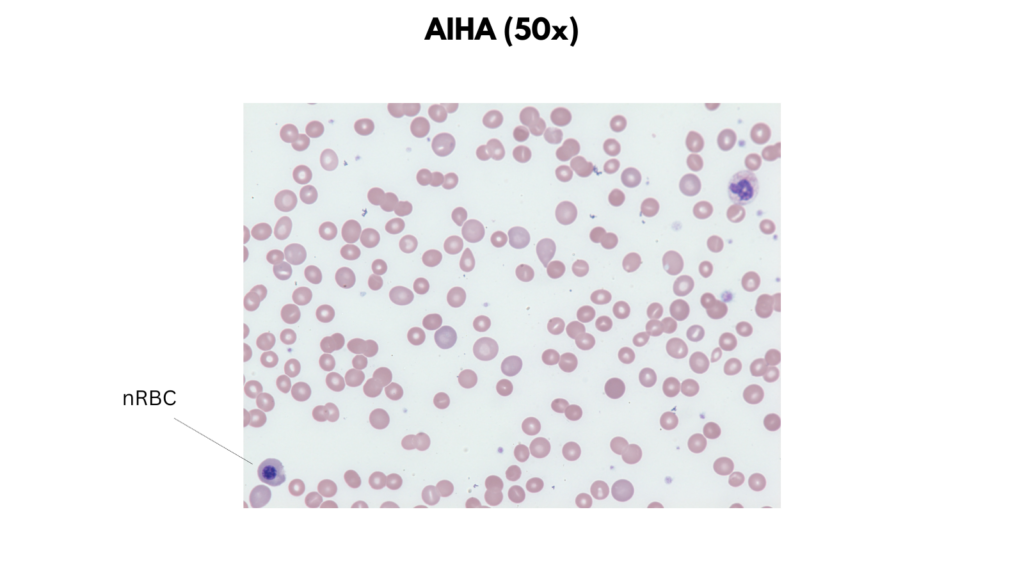
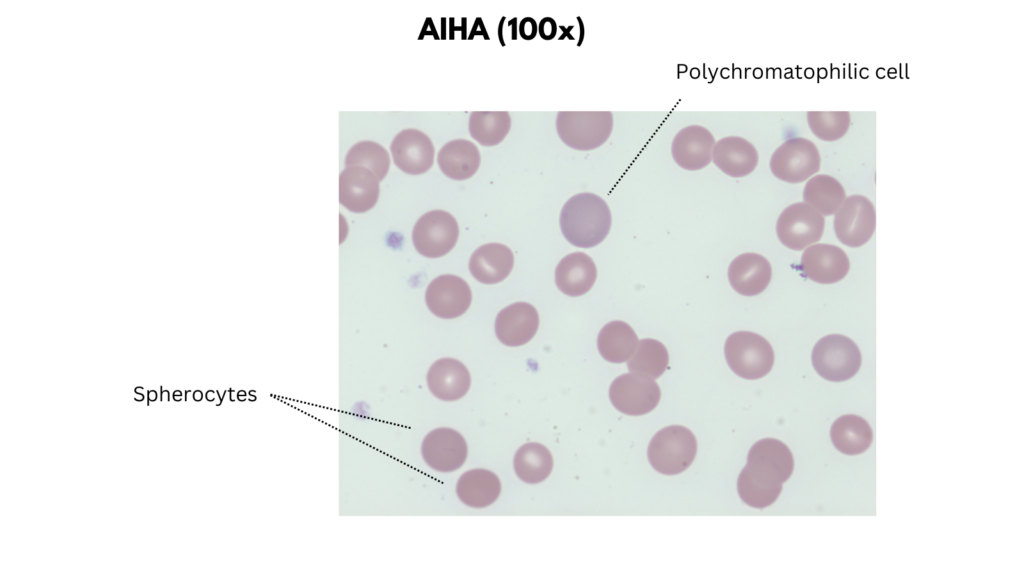
| Warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia | Size +/- Microcytosis Anisocytosis (from spherocytes + reticulocytes) Staining Hyperchromia (loss of central pallor) Increased polychromatophilic cells Shapes Spherocytes Inclusions Typically none |
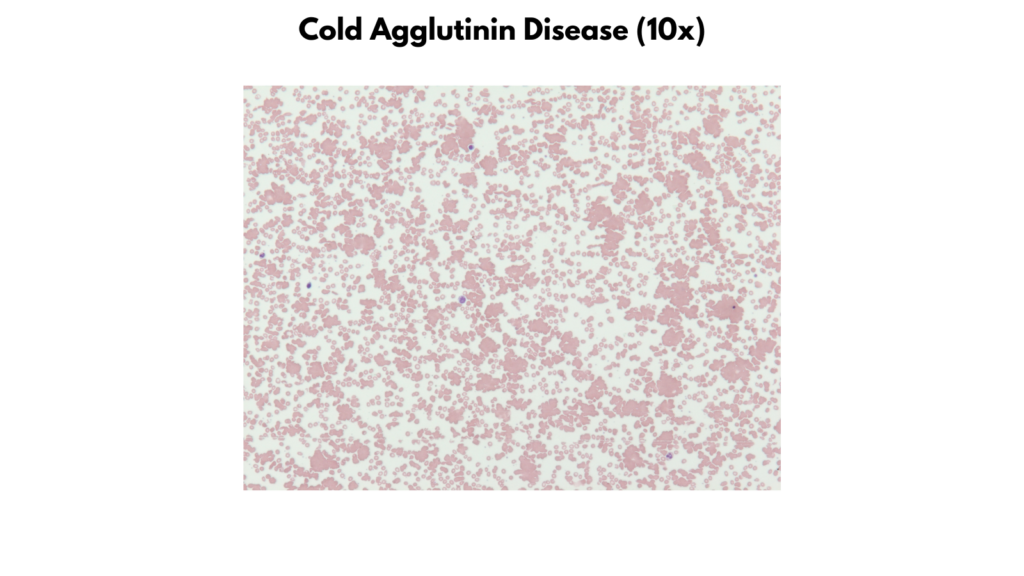
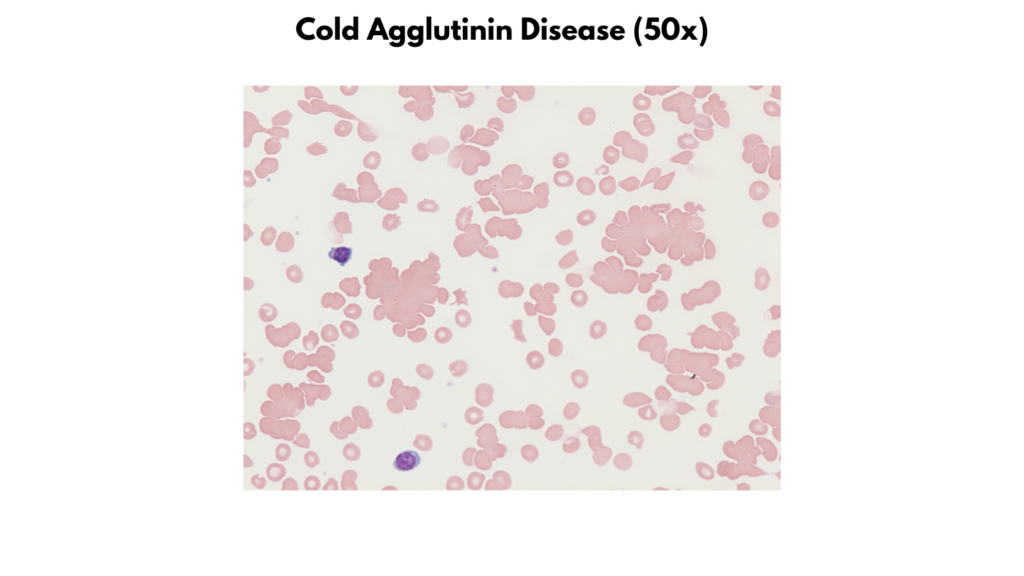
| Cold agglutinin disease | Size Normal Staining Mostly normochromic Increased polychromatophilic cells Shapes Normal Inclusions Typically none Other: RBC agglutination |
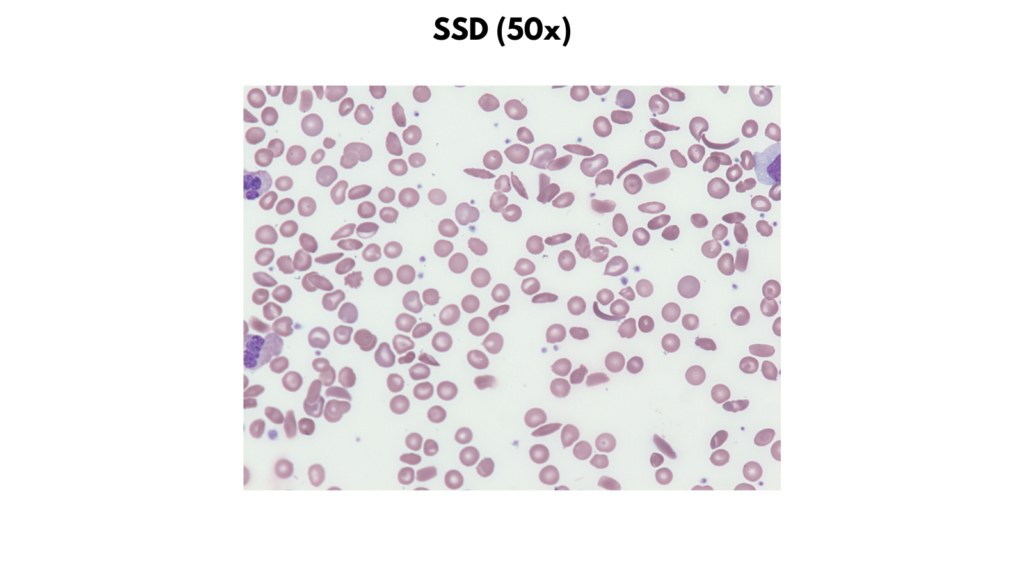
| Sickle cell disease | Size Normal Staining Loss of central pallor in sickle forms Increased polychromatophilic cells Shapes Irreversibly sickled cells Boat cells Inclusions Nucleated RBCs Howell-Jolly bodies Basophilic stippling |
| Hereditary spherocytosis | Size +/- Microcytosis Anisocytosis (from spherocytes + reticulocytes) Staining Hyperchromia (loss of central pallor) Increased polychromatophilic cells Shapes Spherocytes Inclusions Typically none |
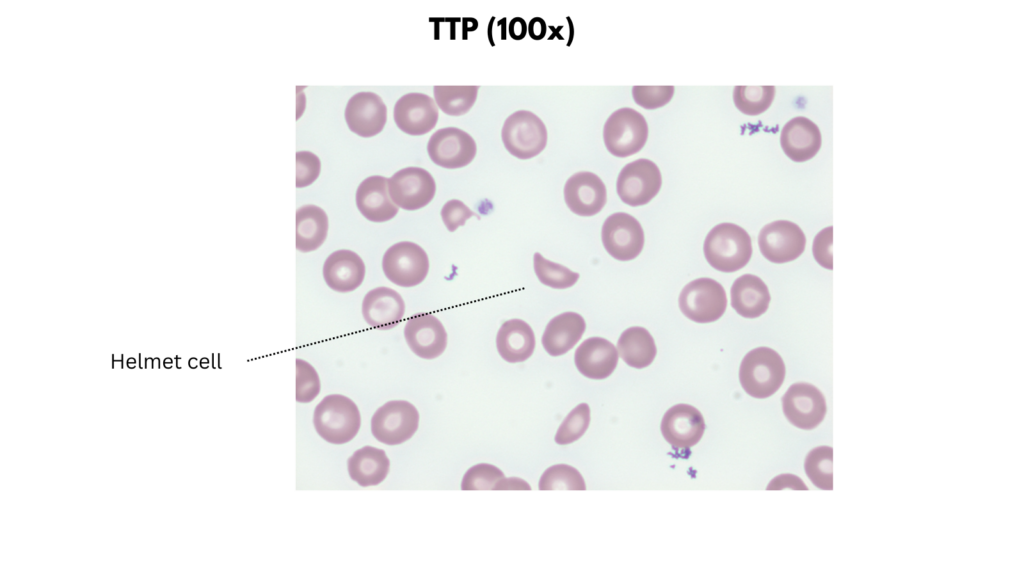
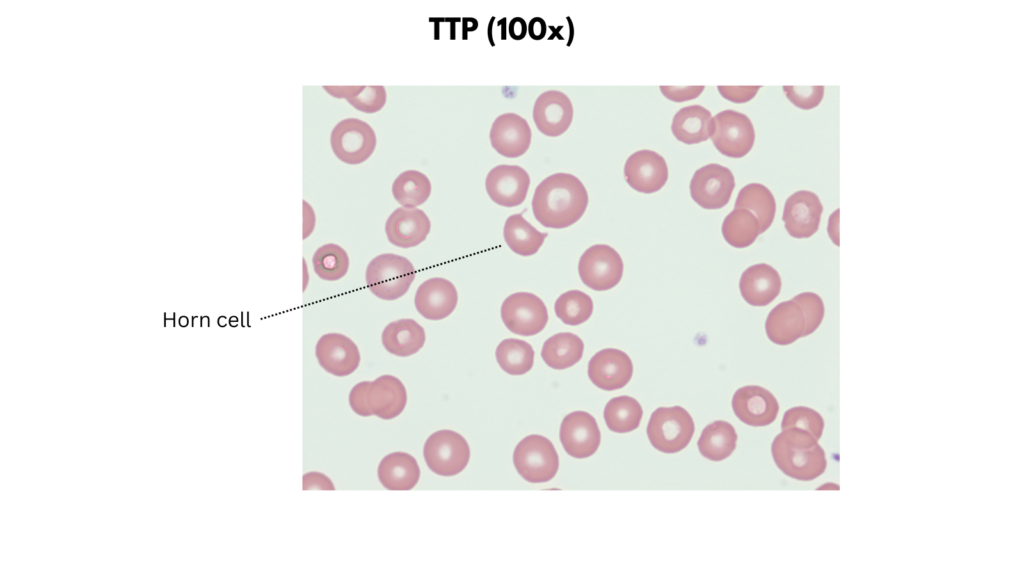
| Thrombotic microangiopathy | Size Typically normal Staining Normal central pallor Increased polychromatophilic cells Shapes Schistocytes Inclusions Typically none |
Examples of peripheral smear findings
- Warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia
- Cold agglutinin disease
- Thrombotic microangiopathy
- Sickle cell disease
Additional TBP resources
- Peripheral smears of:
- Graphic on hemolytic markers
- Infographic on TTP
- Infographic on hereditary spherocytosis
- Infographic on valve hemolysis
- Infographic on spur cell anemia
Prev
1 / 0 Next
