Red Cell Staining (Color)
Prev
1 / 1 Next
Prev
1 / 1 Next
Central pallor
- Introduction
- A normal red blood cell has a biconcave disk shape. Because the center is much thinner than the periphery, it creates the illusion of a Hb-free center on a peripheral smear. The area of pallor in its center (about 1/3 of the diameter of the cell) when viewed under the light microscope.
-
-
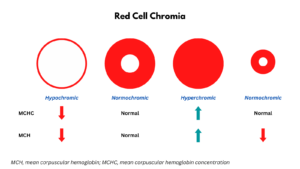
- The area of central pallor may be:
- Normal (normochromia)
- Increased (hypochromia)
- Decreased (hyperchromia)
- The color can be evaluated by the mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC).
- The area of central pallor may be:
-
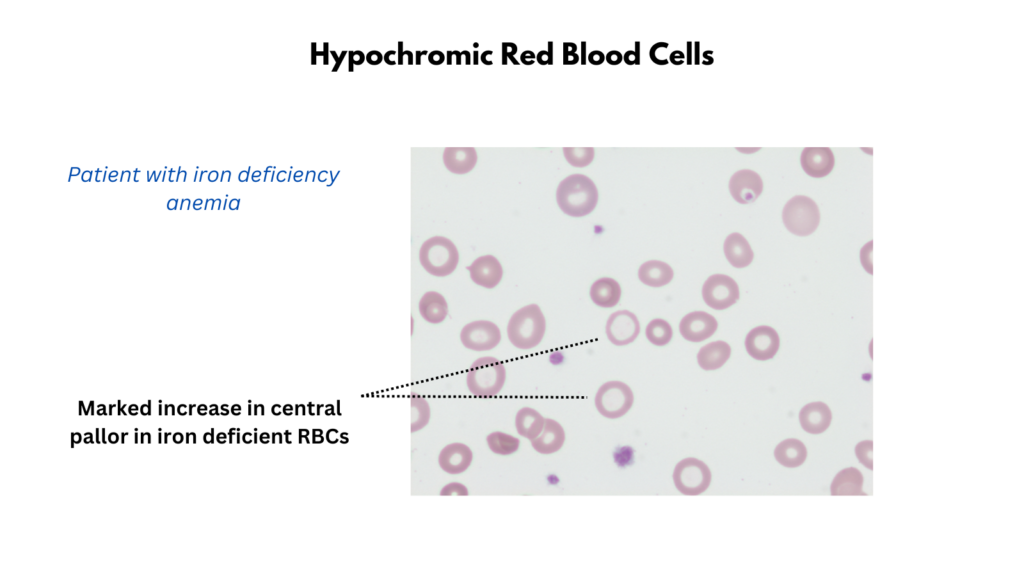
- Hypochromia
- Hypochromic red blood cells have less color (> 1/3 central pallor) than normal when examined under a microscope.
- The decrease in redness is due to a disproportionate reduction of red cell hemoglobin (the pigment that imparts the red color) in proportion to the volume of the cell.
- Hypochromia correlates with a lower than normal MCHC.
- The MCHC, in turn, is helpful in distinguishing between causes of microcytic anemia.
- Differential diagnosis of hypochromia includes:
- Iron deficiency
- Thalassemia intermedia/major
- Anemia of inflammation
- Sideroblastic anemia
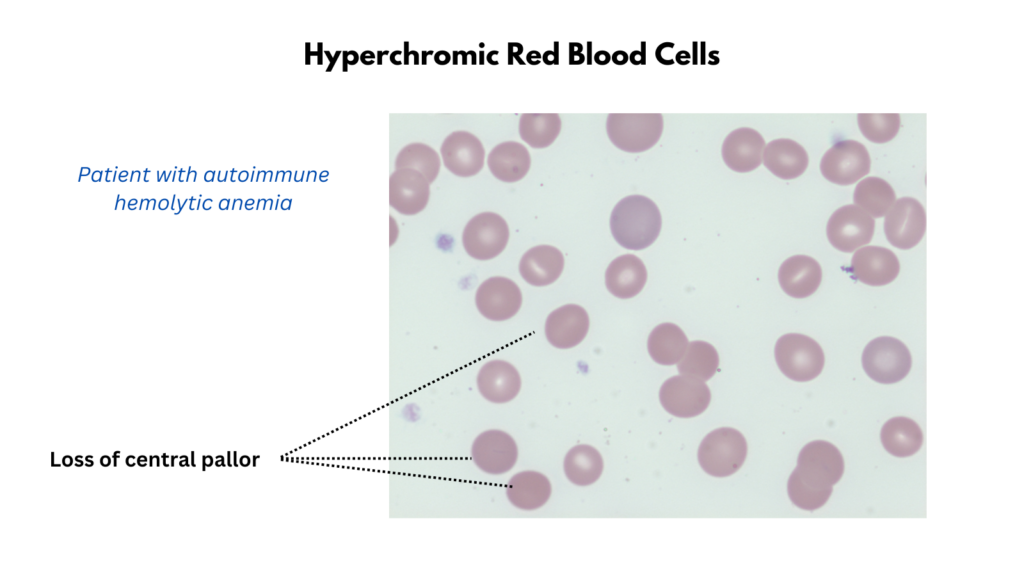
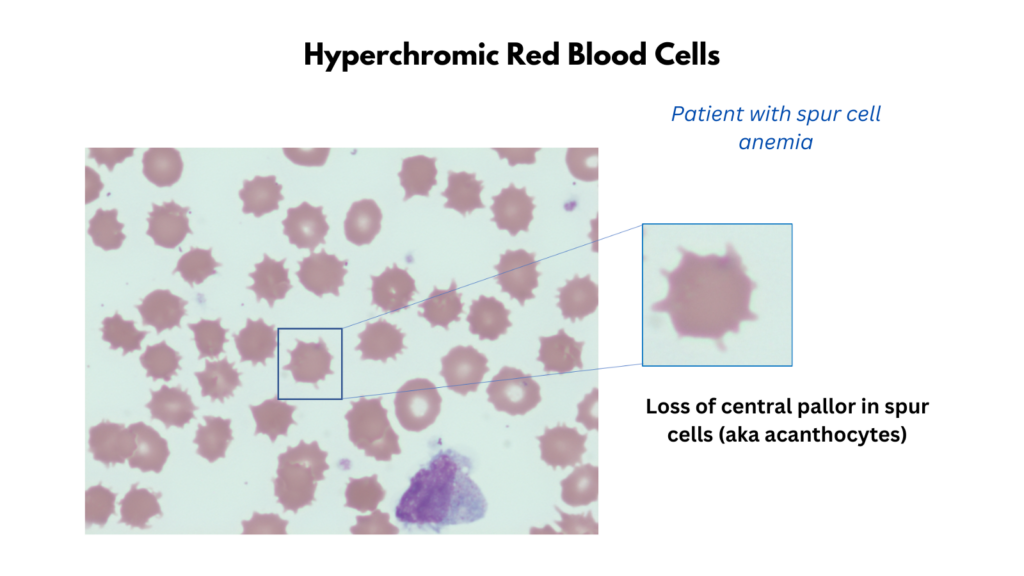
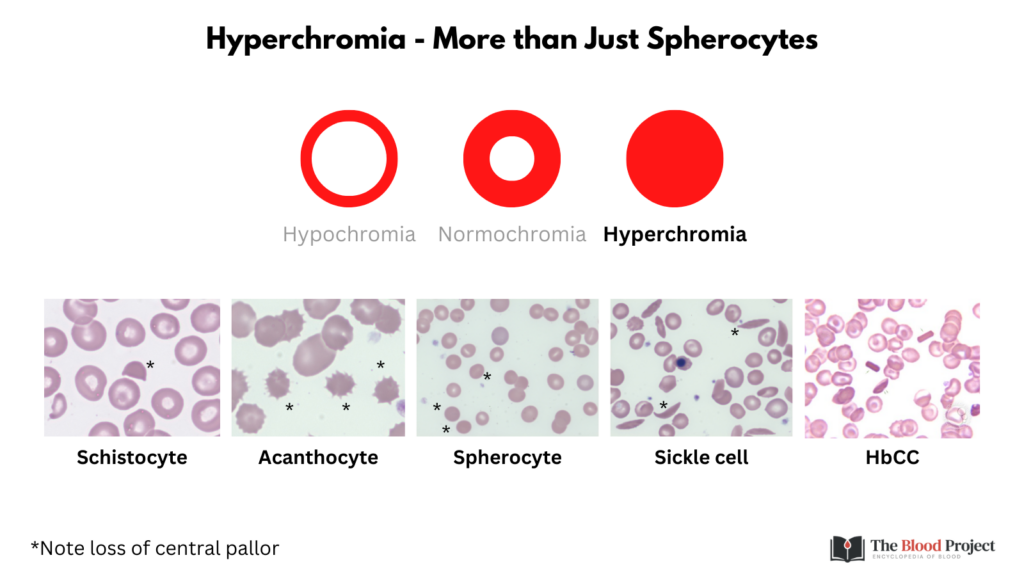
- Hyperchromia
- Refers to an increase in the intensity of red blood cell color.
- The area of central pallor is decreased or gone.
- Correlates with a higher than normal MCHC.
- Hyperchromic cells may be:
- Spherocytes
- Microspherocytes
- Sickle cells
- Spur cells
- Schistocytes
- HbC cells
- Differential diagnosis includes:
- Spurious
- Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
- Hereditary spherocytosis
- HbC
- Spur cell anemia
- Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia
Polychromatophilia
- Immature non-nucleated red cells with a blue hue in their cytoplasm.
- The blue may be barely visible or may be marked.
- Polychromatic red cells are typically larger than normal red cells.
- They tend to lack central pallor.
- When stained with supravital dyes the remaining mRNA and ribosomes give the red cells a “reticular” mesh-like network, hence the name “reticulocyte”.
- Of note, white the vast majority of polychromatophilic cells are reticulocytes (as defined by the presence of reticulum on a reticulocyte stain), not all reticulocytes are recognized as polychromatophils on the Wright-Giemsa stain.
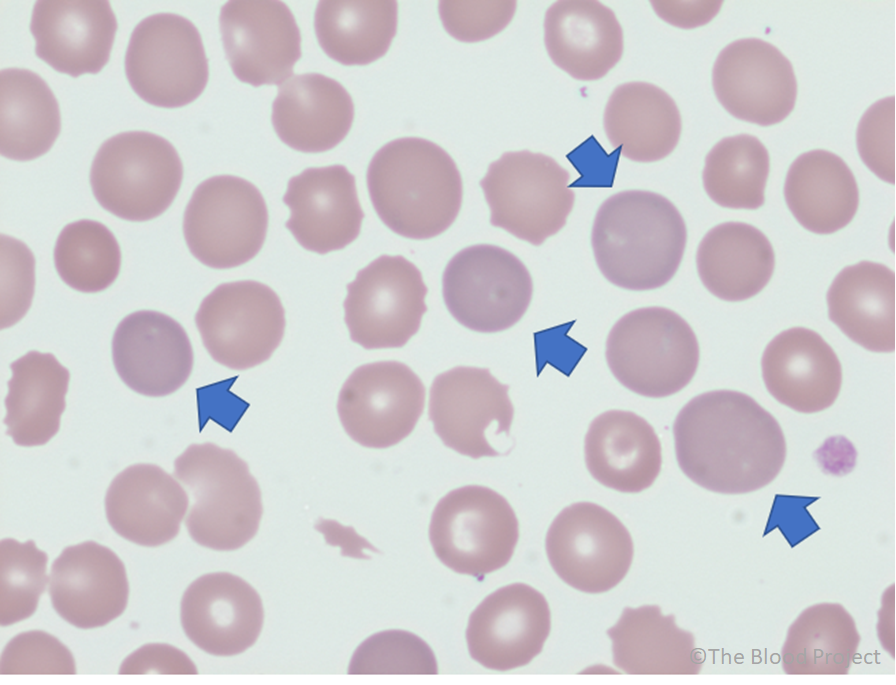
Peripheral smear from a 25-year-old woman with GI bleed shows multiple polychromatophilic red cells (polychromatophilia) 100x (oil).
Prev
1 / 1 Next
