Quiz – Platelets high and low

By William Aird
Abbreviations:
Hb – hemoglobin
Hct – hematocrit
MCH – mean corpuscular hemoglobin
MCHC – mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration
MCV – mean cell colume
RBC – red blood cell count
RDW – red blood cell distribution width
RDW-CV – RDW coefficient of variation
RDW-SD – RDW standard deviation
Note: The terms MCV, MCH and MCHC are all mean values and by definition apply to populations of red cells. To simplify matters, we use the term more loosely to include descriptions of single cells. For example, we may refer to a large red cell as one with a high MCV, or a cell with increased central pallor as one with a low MCHC.
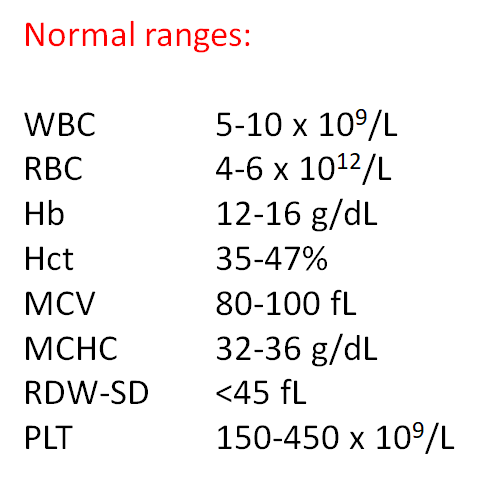
Question 1
What is the principle growth factor that regulates the platelet count?
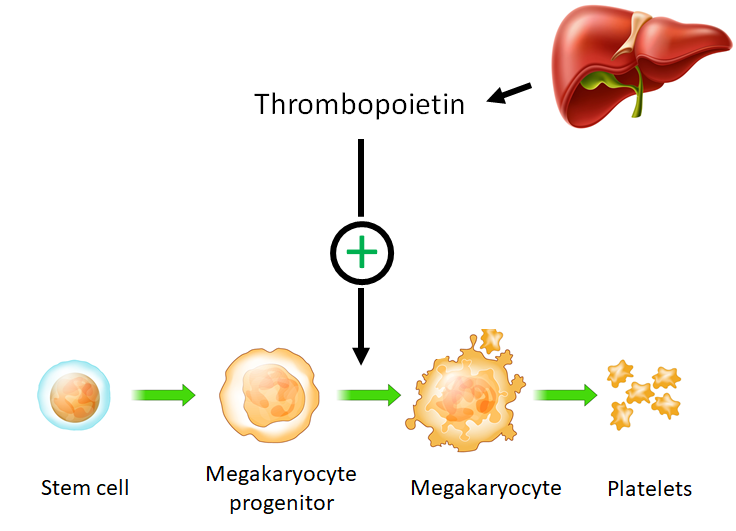
Question 3
How is extreme thrombocytosis defined?
Patients with extreme thrombocytosis have been referred to as platelet millionaires! That is because 1000 x 109/L is 1 million/ul.

Question 4
True or false: there is no evidence that secondary (reactive) thrombocytosis is associated with an increased risk of thrombosis.
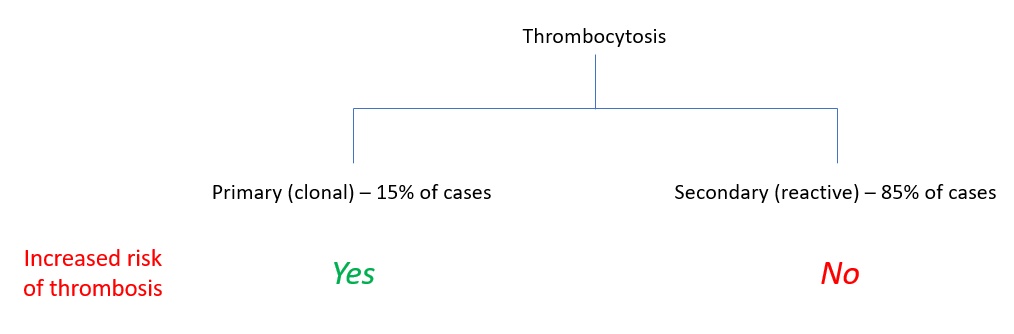
Question 2
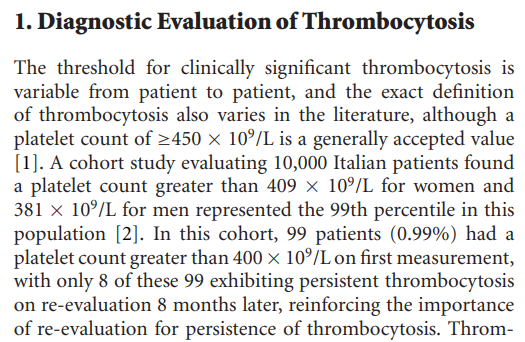
How is thrombocytosis defined?
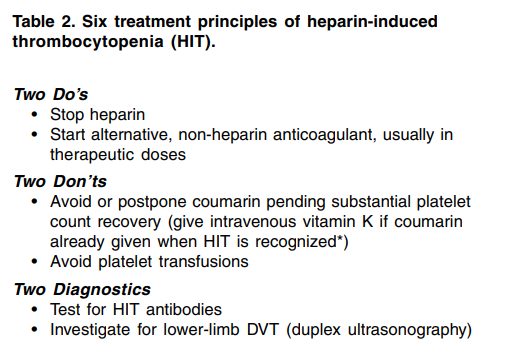
What are treatment goals in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia?
In primary thrombocytosis:
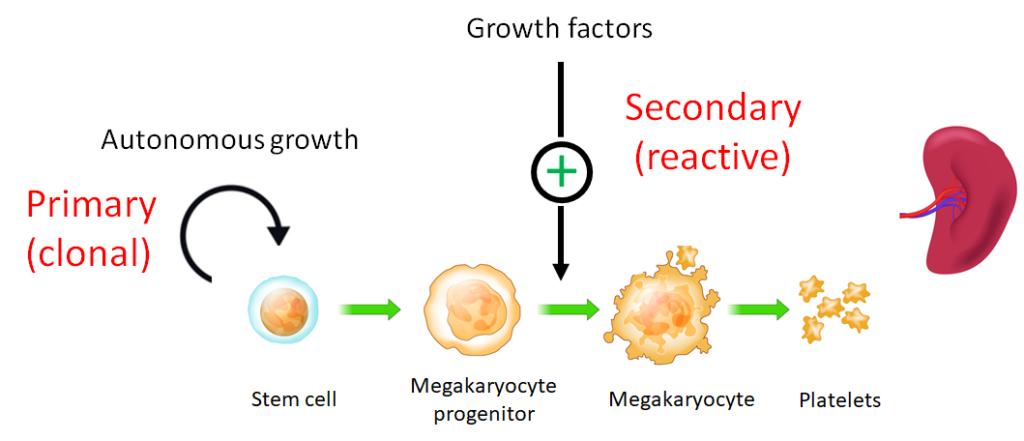
True of false: patients admitted to the ICU may have thrombocytopenia, but thrombocytosis is virtually unheard of.
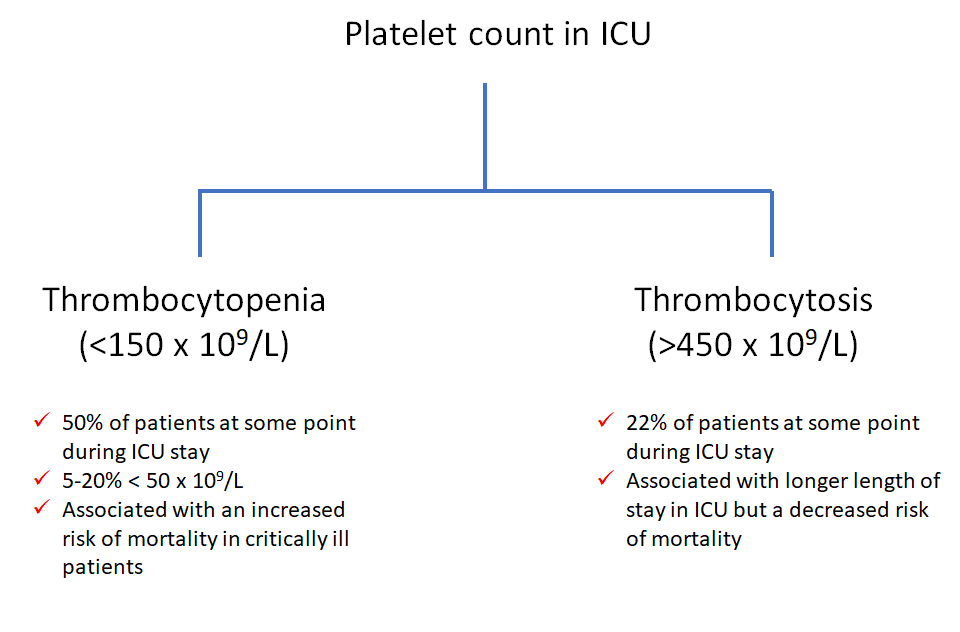
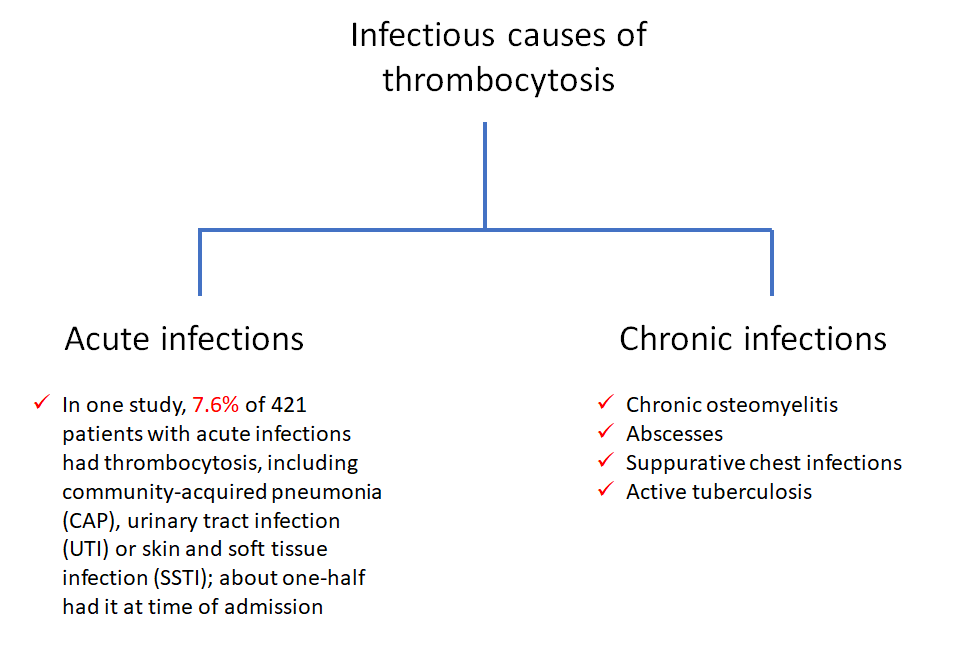
True or false: infection-related secondary (reactive) thrombocytosis is only associated with chronic infections.
What percentage of patients with newly diagnosed essential thrombocythemia have thrombocytosis?
Mean platelet lifespan is about:
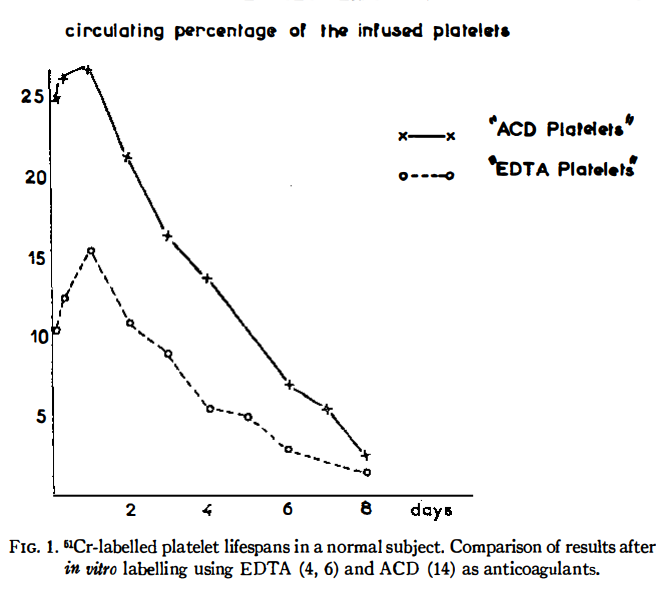
How are levels of circulating thrombopoietin regulated?
What is the frequency of splenomegaly in essential thrombocythemia?
Splenomegaly is more common in myelofibrosis than in essential thrombocythemia or polycythemia vera
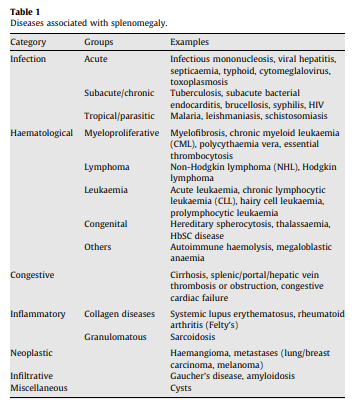
A reminder of the differential diagnosis of splenomegaly:
In a patient with thrombocytosis, the presence of pencil cells on the peripheral smear suggest which etiology for the elevated platelet count:
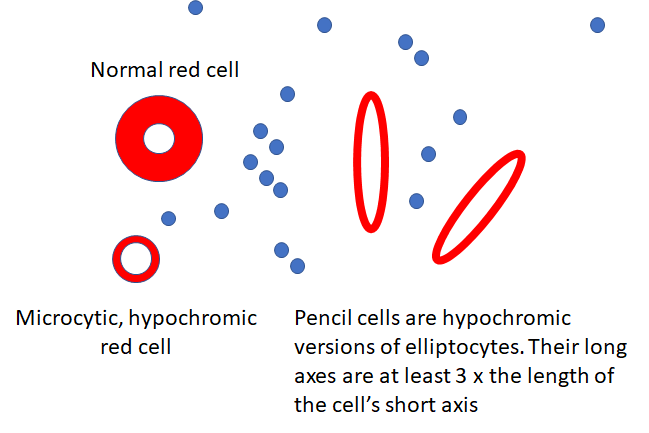
Why would you ever order a von Willebrand disease screen in a patient with thrombocytosis?
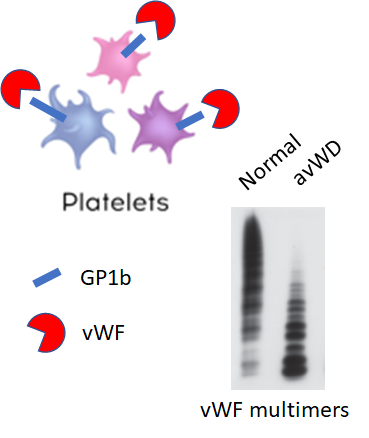
What are recognized complications of essential thrombocythemia?
What genetic tests are recommended in patients with suspected essential thrombocythemia (together or sequentially)?
Patients with essential thrombocythemia may carry JAK2 (V617F), an MPL substitution, or a calreticulin gene (CALR) mutation. These are called driver mutations. Each genotype is associated with specific clinical characteristics, including differences in symptomatic burden, hematological values, and risk of thrombosis and bleeding.
| Jak2 | Mpl | CALR | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prevalence | 60% of patients with essential thrombocythemia | 1-4% of patients with essential thrombocythemia | 25% of patients with essential thrombocythemia |
| Age | X | X | Younger vs JAK2Val617Phe genotype |
| Platelet count | X | X | Higher vs JAK2Val617Phe genotype, similar to Mpl-mutated genotype |
| Hemoglobin | X | X | Lower vs. JAK2Val617Phe genotype |
| Thrombosis risk | X | X | Lower vs. JAK2Val617Phe and MPL-mutated genotypes |
| Leukemic transformation | X | X | No difference vs. AK2Val617Phe genotype |
| Fibrotic transformation | Higher vs. JAK2Val617Phe genotype | No difference vs. AK2Val617Phe genotype |
X
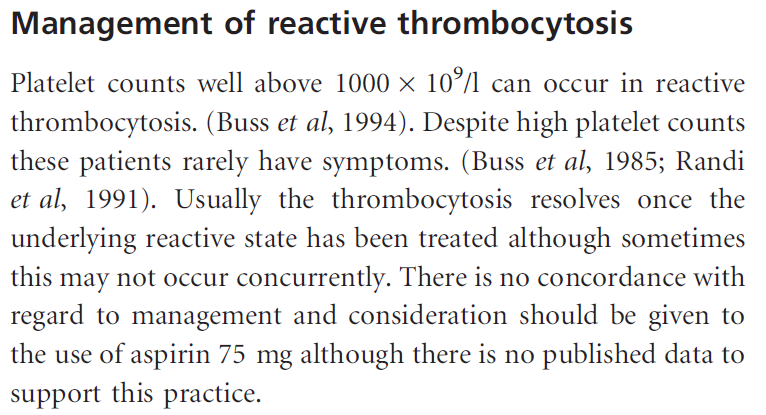
True or false: aspirin is recommended in patients with secondary (extreme) thrombocytosis.
In the interest of full disclosure, the single guideline that is focused on “investigation and management of adults and children presenting with a thrombocytosis” from 2010 suggests considering the use of aspirin in patients with secondary (reactive) thrombocytosis, but it is doubtful that most clinicians would agree with this:
In a patient with thrombocytosis, the presence of Howell Jolly bodies on the peripheral smear suggest which etiology for the elevated platelet count:
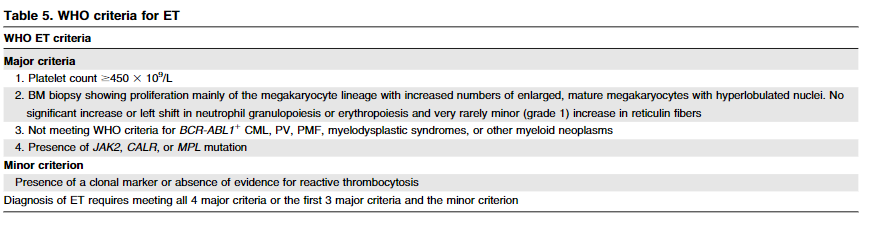
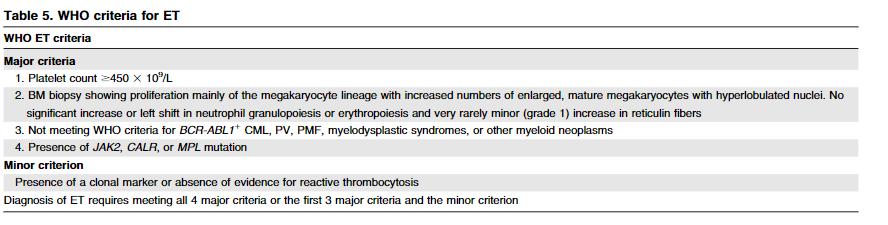
2016 World Health Organization (WHO) Criteria for diagnosis of ET includes major and minor criteria. Which three major criteria are always required?
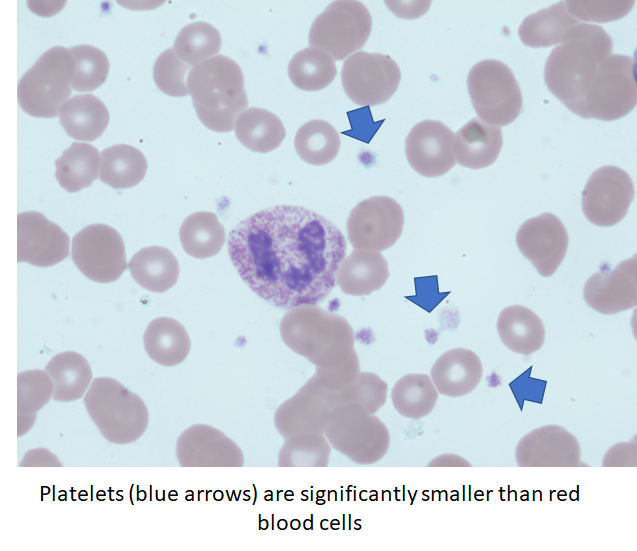
Platelets are:
From D. Saintillan:
The in vivo production of platelets takes place inside bone marrow, where large cells known as megakaryocytes develop long tubular membrane projections, or proplatelets, which continuously break up into small fragments destined to mature into functional platelets and enter the blood stream. The formation and growth of these tubular structures and their subsequent fragmentation are driven by ATP-powered processes involving biopolymers and molecular motors.
From Machlus and Italiano:
To assemble and release platelets, MKs become polyploid by endomitosis (DNA replication without cell division) and then undergo a maturation process in which the bulk of their cytoplasm is packaged into multiple long processes called proplatelets, and the nucleus is extruded. An MK may extend 10–20 proplatelets, each of which starts as a blunt protrusion that over time elongates, thins, and branches repeatedly. Platelets form selectively at the tips of proplatelets. As platelets develop, they receive their granule and organelle content as streams of individual particles transported from the MK cell body
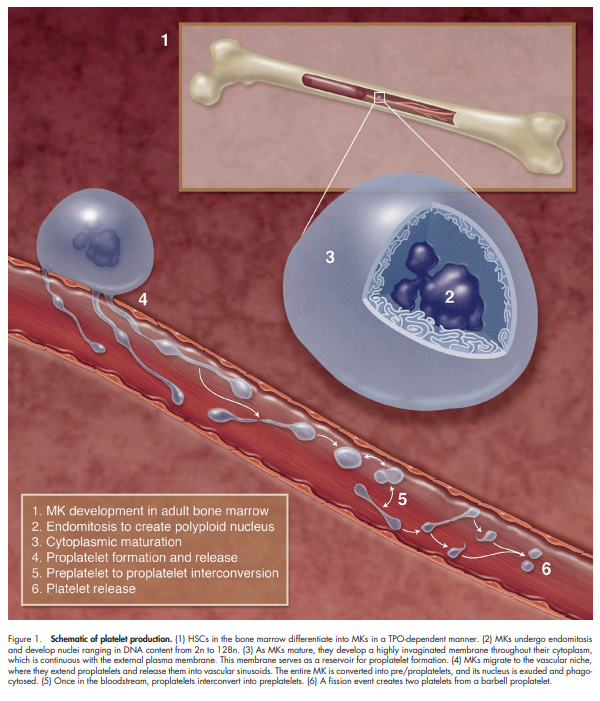
How large is a platelet?

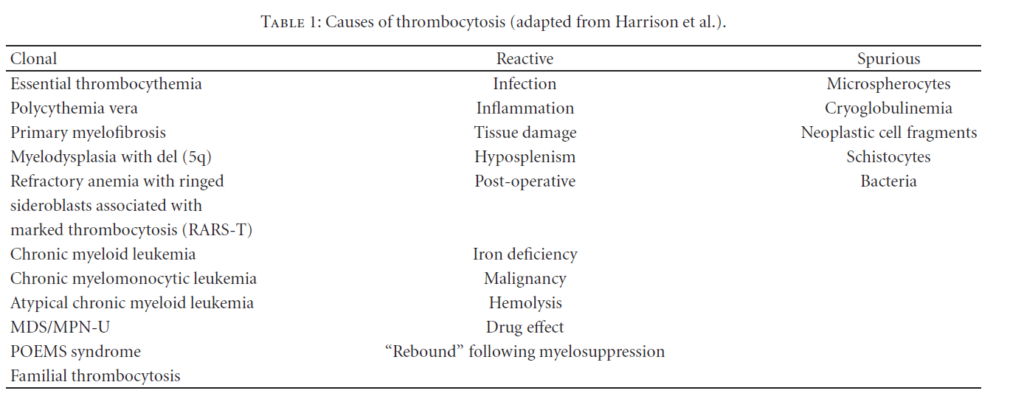
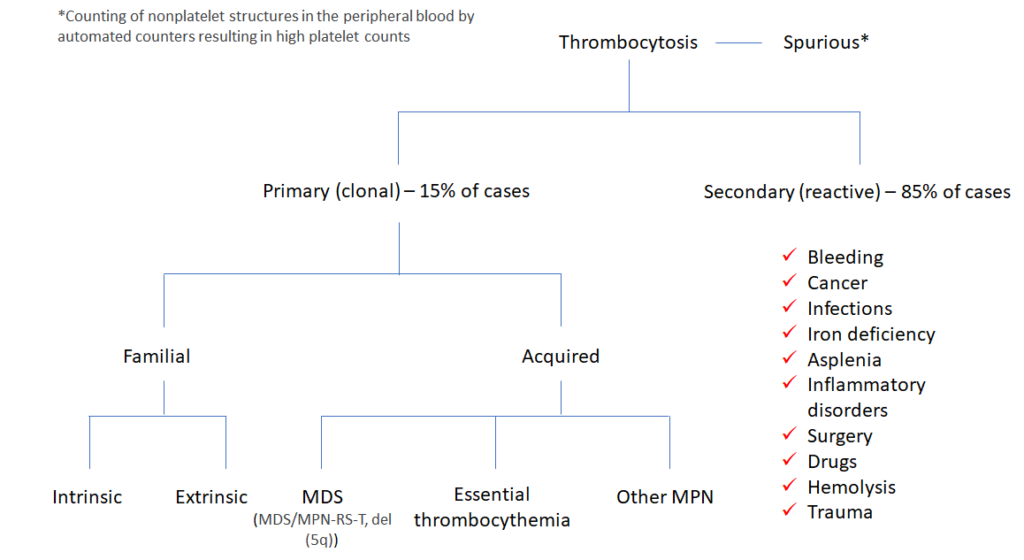
Which of the following are causes of primary thrombocytosis?
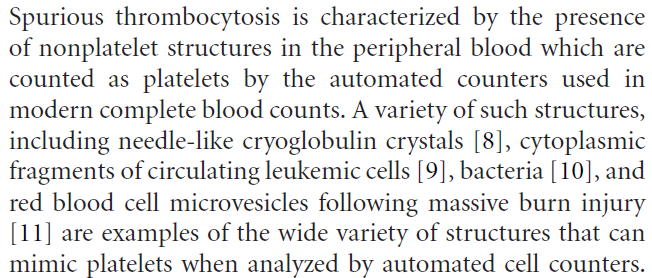
The following are causes of spurious thrombocytosis:
Question 8
Iron deficiency may be associated with:
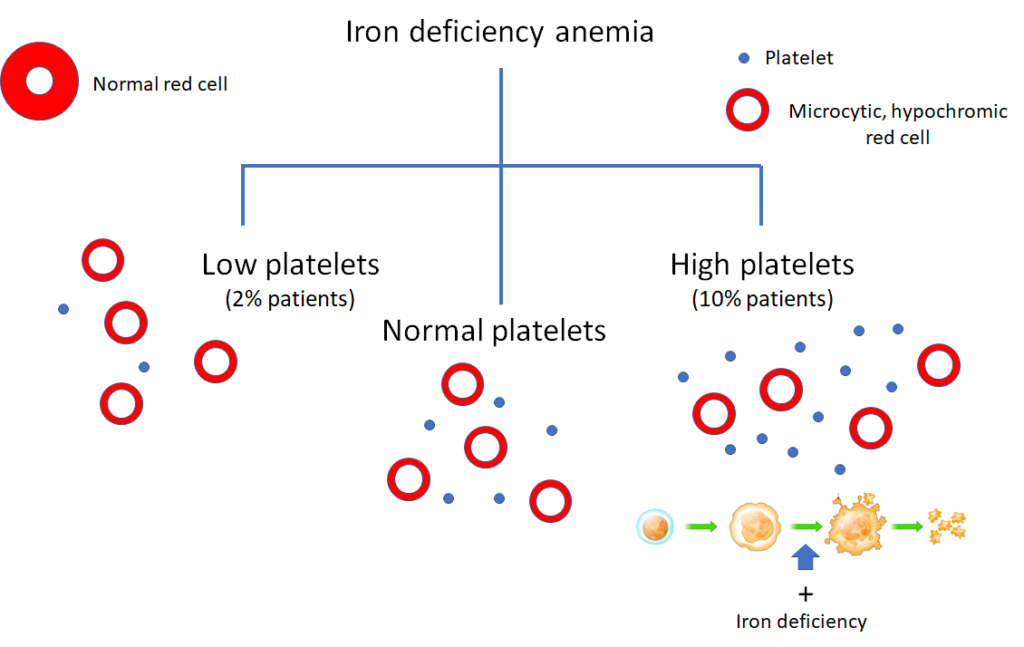
Question 9
In a patient with a platelet count of 1000 x 109/L, what parameter do you need to calculate the plateletcrit?
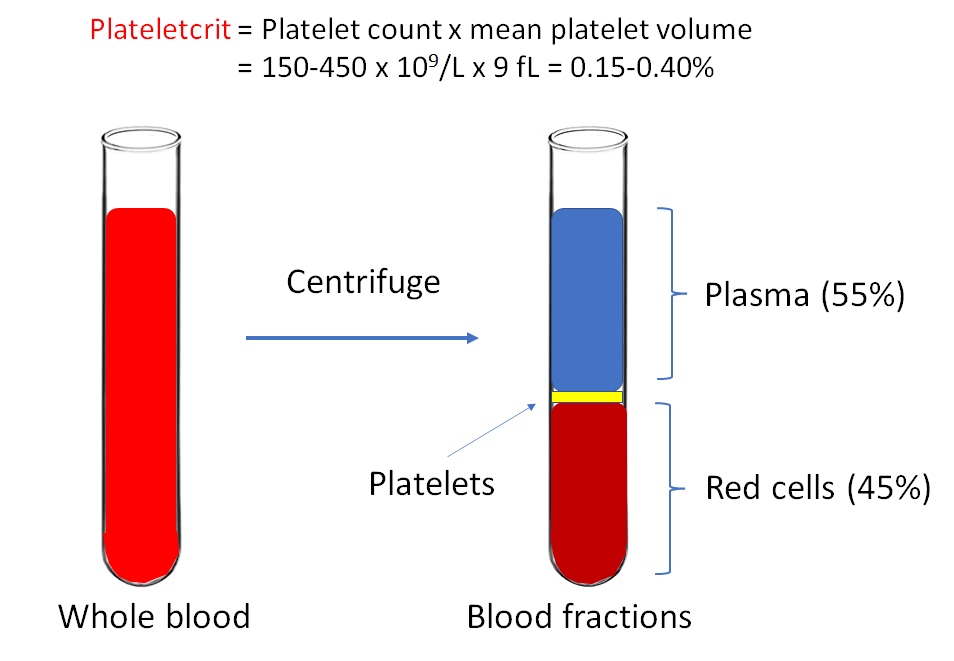
Question 5
What is the preferred treatment for secondary (reactive) thrombocytosis?
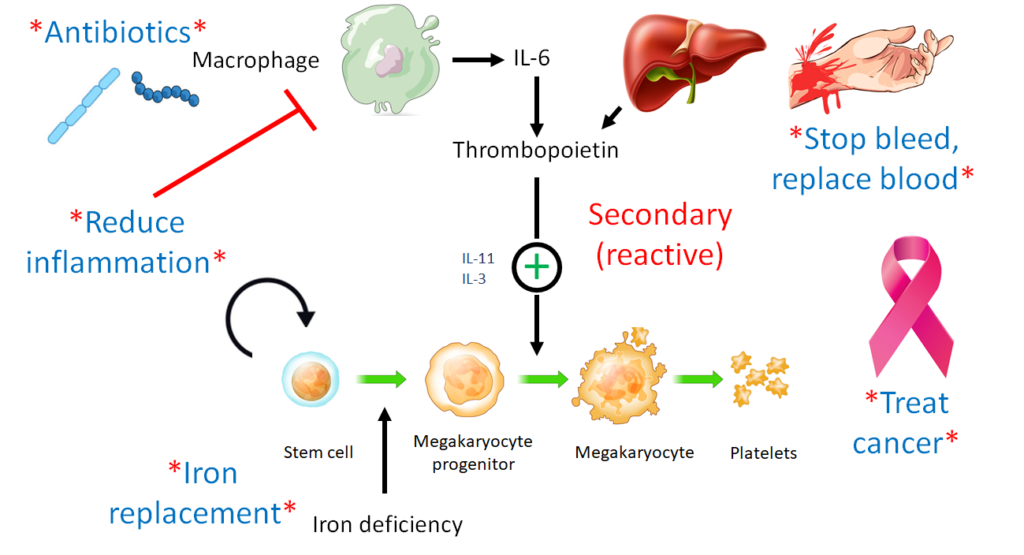
Which is more common:
Question 6
Which of the following are established causes of secondary (reactive) thrombocytosis?
What is heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)?
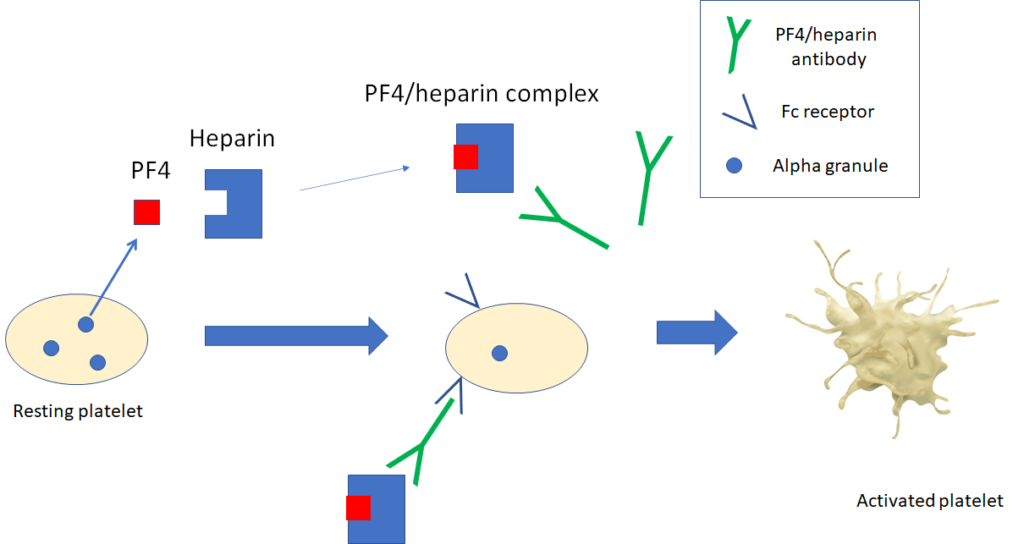
When does the platelet count typically begin to drop in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (following initiation of heparin)?
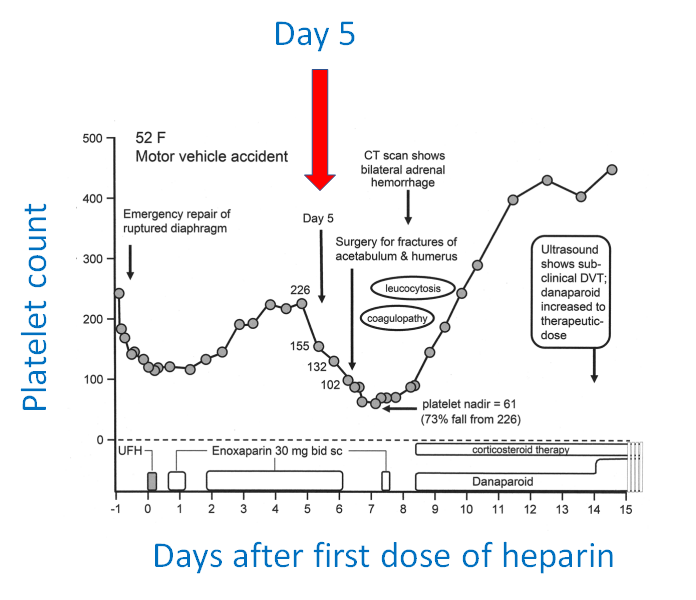
What is spontaneous heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)?
The PLASMIC score is used to estimate pretest probability of which condition?
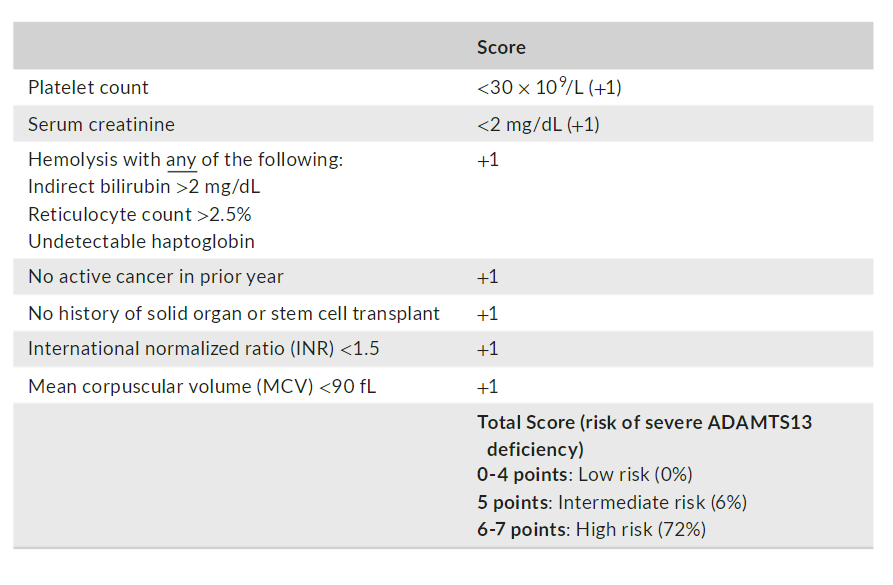
n a recent publication, high scores of 6- 7 versus low/intermediate scores of 0- 5 predicted severe ADAMTS13 deficiency with a positive predictive value of 72%, negative predictive value of 98%, sensitivity of 90%, and specificity of 92%
Which type(s) of heparin is/are associated with the highest rate of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia?
True or false: heparin-induced thrombocytopenia may be associated with a drop in platelet count within the normal platelet count range.
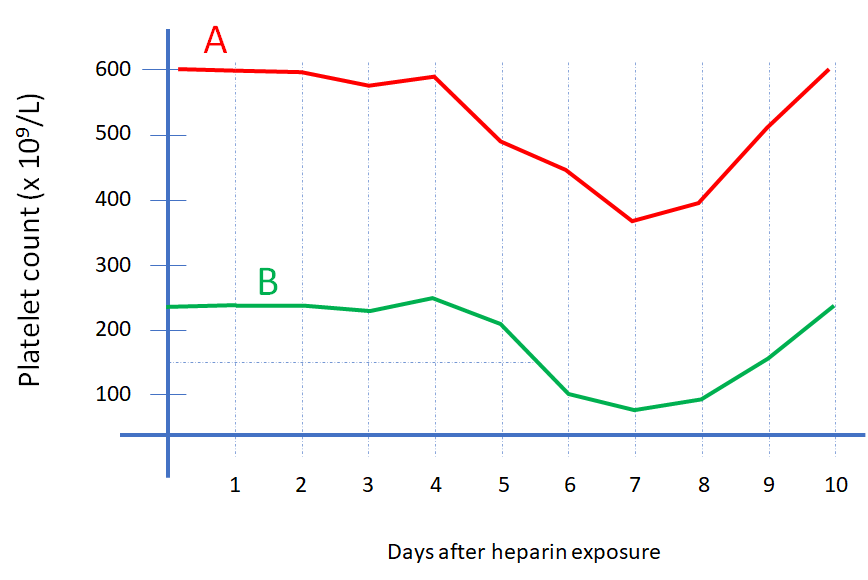
In heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, what is the average lag time between detection of HIT antibodies and the clinical manifestations of thrombocytopenia and/or thrombosis?
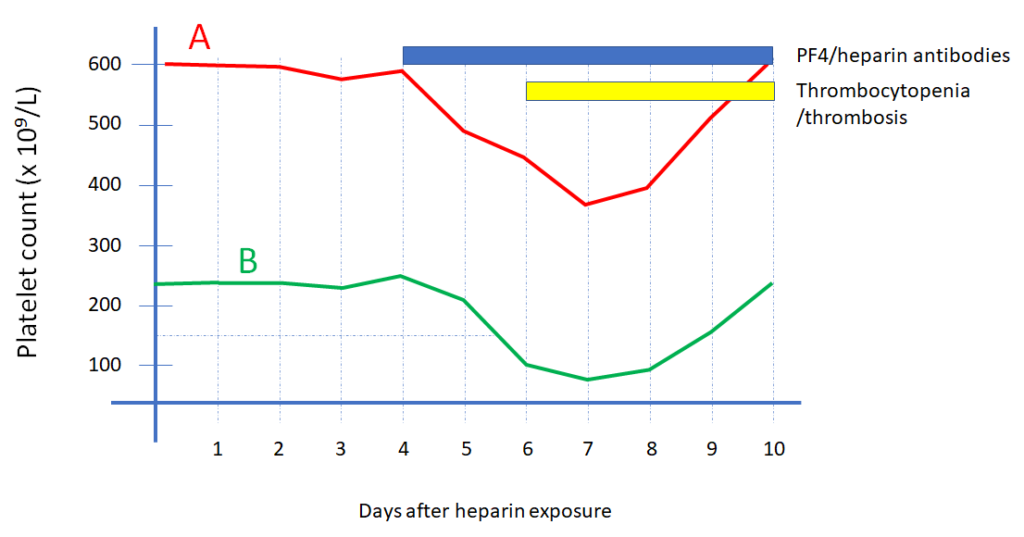
Which the following statement(s) is/are true:
True of false: heparin-induced thrombocytopenia does not occur with prophylactic low dose unfractionated heparin.
Which 2 patient populatiokns ahve the highesst risk of developing heparin-induced thrombocytpoeani?
What is the median platelet count (109/L) in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia?
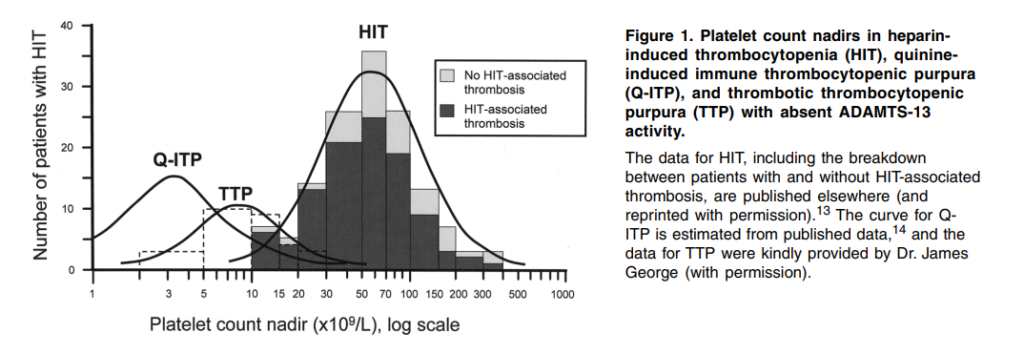
The 4T score is best for:
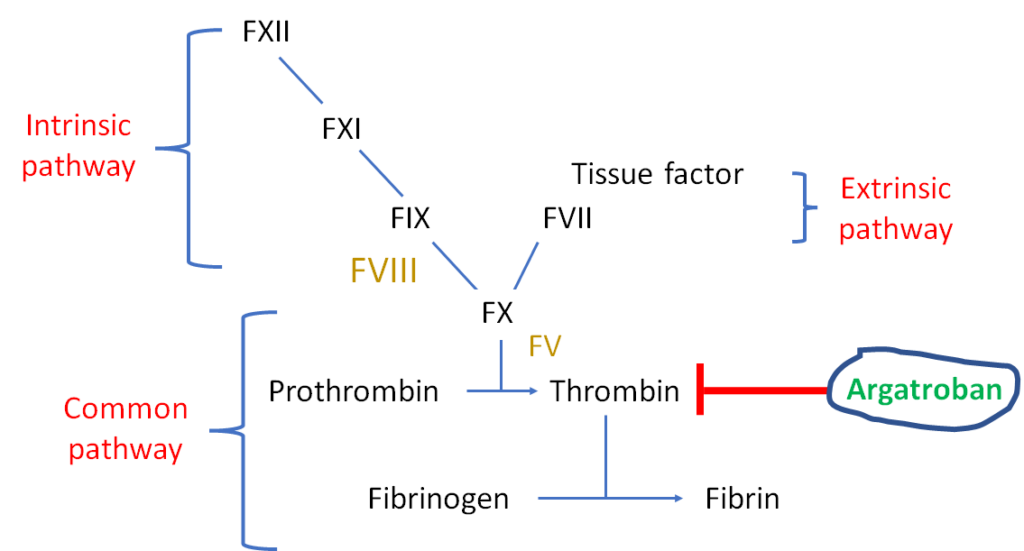
What is Argatroban?
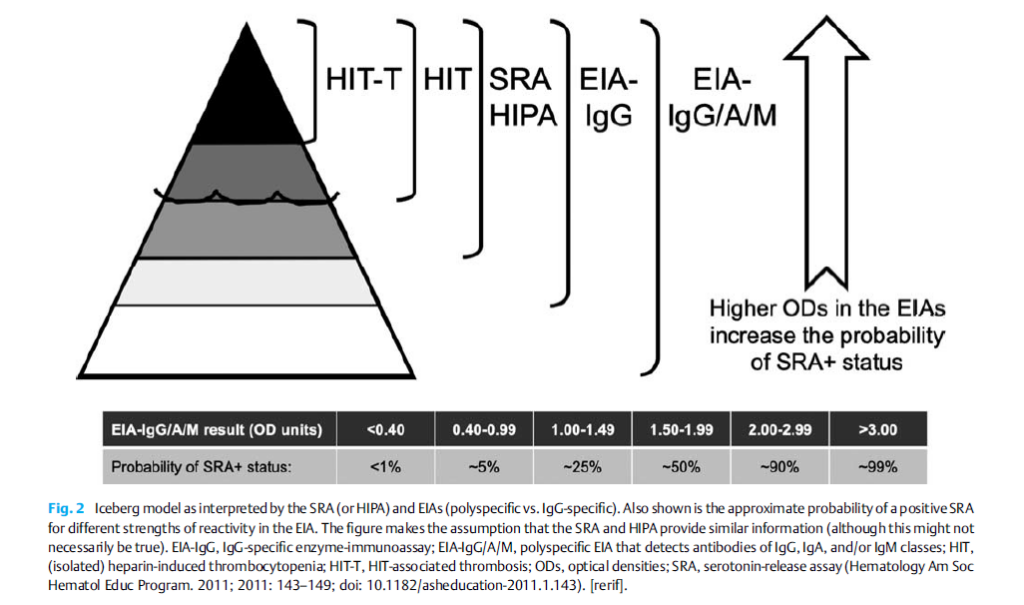
True or false: a diagnosis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia can be made without laboratory evidence of antiPF4/heparin antibodies
Question 10
What is the typically timing for the onset of thrombocytosis after major surgery?
What is the frequency of thrombosis in patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia?
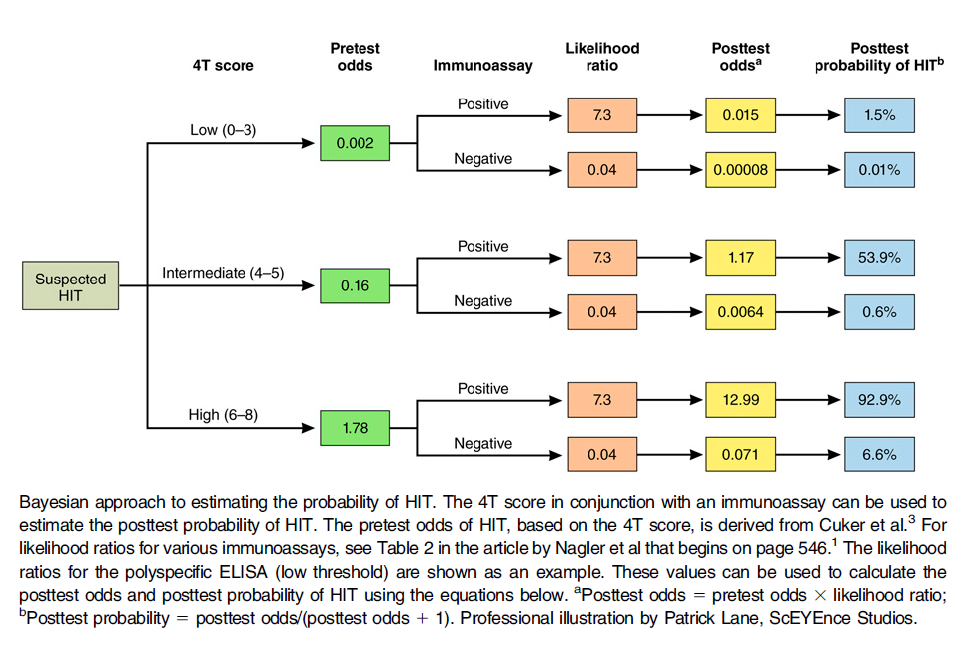
4Ts score estimates pretest probability of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Which of the following are included in the 4Ts score?
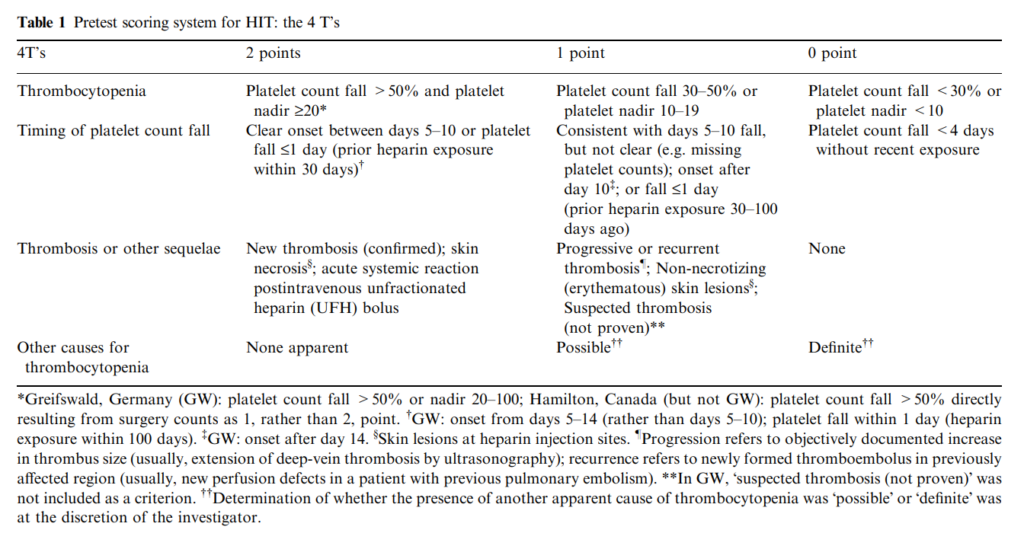
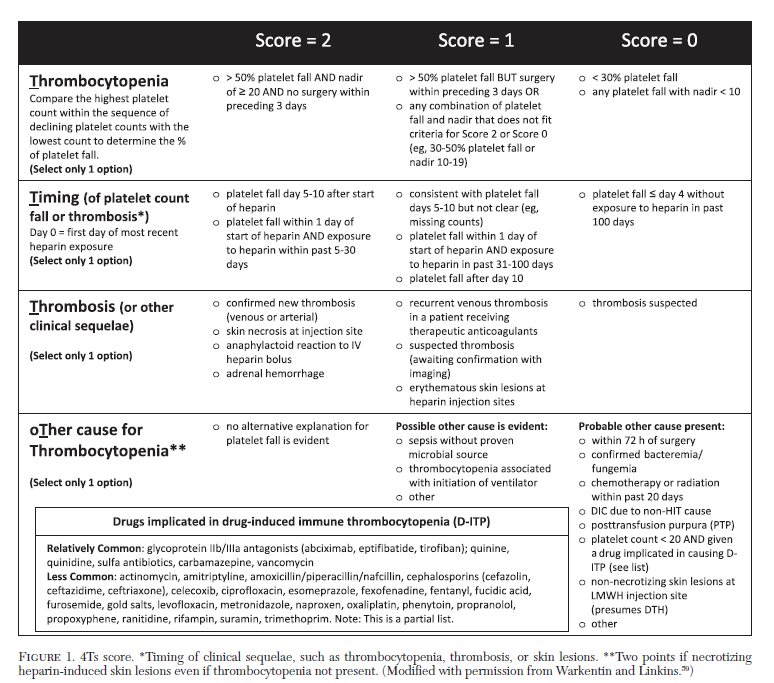
True of false: Some patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and positive immunoassay never develop thrombosis.
If a patient is taking coumadin at the time heparin-induced thrombocytopenia is diagnosed, in addition to stopping heparin what would you recommend?
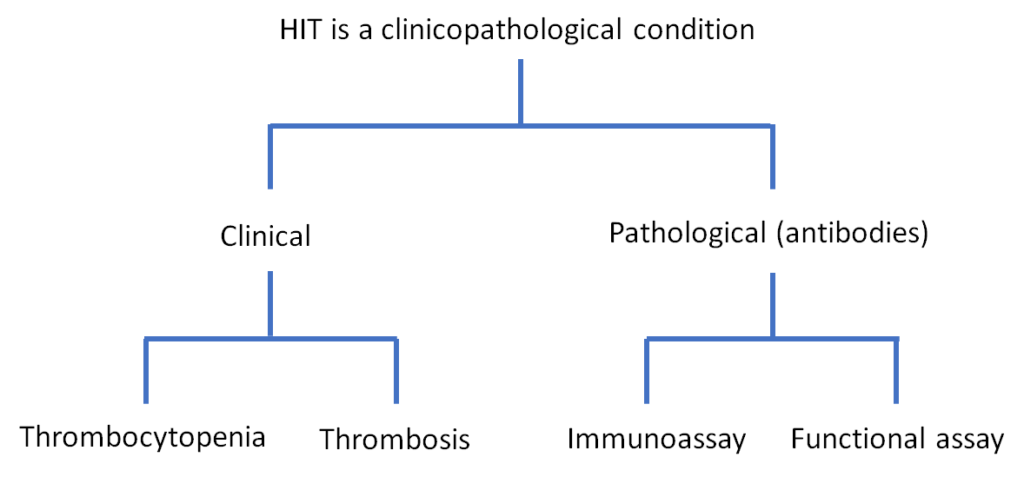
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia has been termed a model “clinico-pathological” disorder. What is/are the pathological feature(s) referred to by this term?
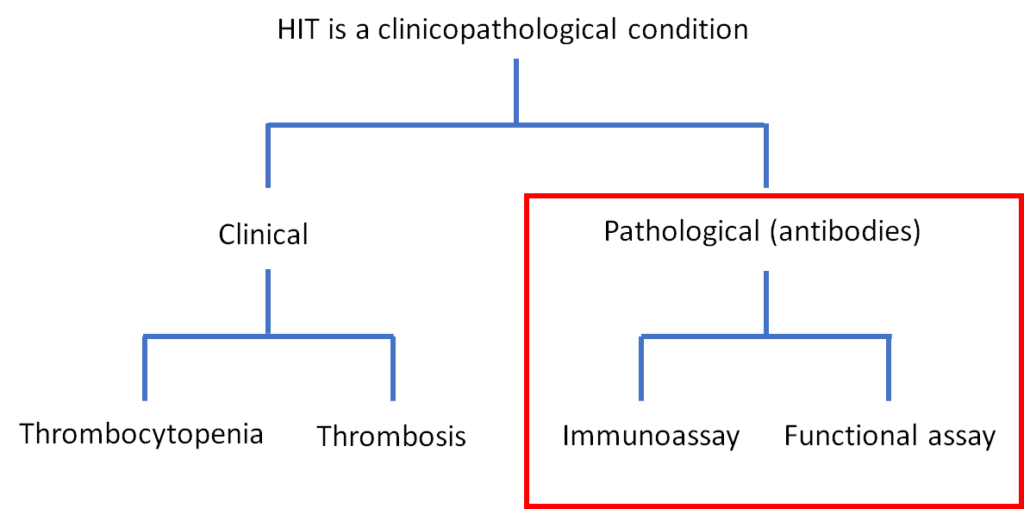
True or false: heparin exposure often triggers an anti-PF4/H immune response that does not result in HIT.
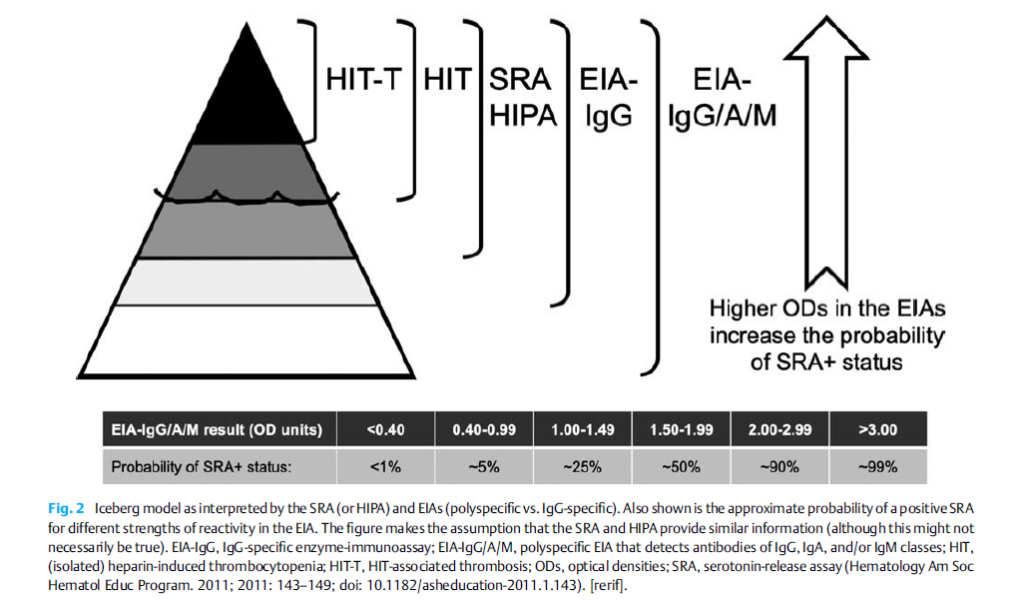
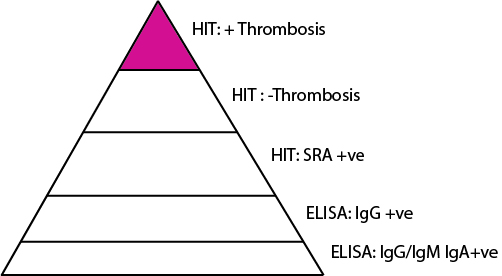
What’s more a more common complication in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia?
True of false: Not all anti-PF4/heparin antibodies are pathogenic; some do not result in HIT?
True or false: some patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura are not critically ill and have only thrombocytopenia and microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (without evidence of end organ damage).
In patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, how long does it take for the antibodies to disappear as measured by immunoassay?
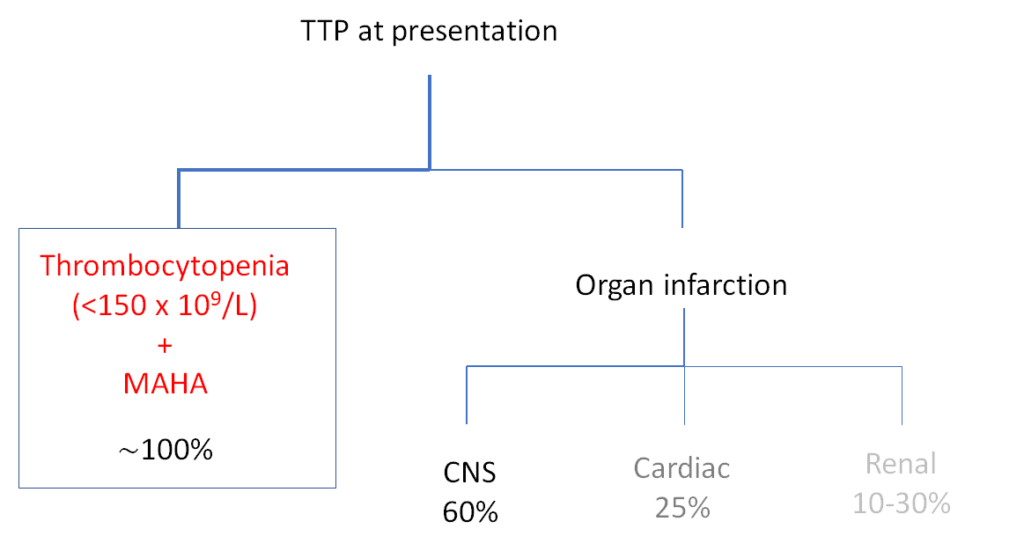
Which is more specific for the diagnosis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia?
What is the cause of acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenia purpura?
What is the normal function of ADAMTS13?
Which of the following are part of the classic trial in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura?
What is the mortality associated with untreated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura?
In addition to thrombocytopenia and anemia, what serum lab abnormalities might you see in a patient with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura?
Can heparin-induced thrombocytopenia occur when platelet activation assays are repeatedly negative (SRA-negative HIT)?
True of false: the number of schistocytes on peripheral smear are generally higher in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura compared to disseminated intravascular coagulation
What is the sensitivity of the serotonin release assay in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia?
Which condition is associated with massive systemic activation of secondary hemostasis with generation of fibrin thrombi?
True or false: HLH may be associated with thrombocytopenia?
What is the definition of severe ADAMTS13 deficiency?
The ADAMTS13 activity assay is usually sent out to specialized lab and it takes several days for the results to come back. True or false: treatment for suspected thrombocytopenic purpura should be withheld while waiting for the result.
Diagnostic samples for ADAMTS13 from a patient with suspected thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura should be obtained:
How common is the classic pentad in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura?
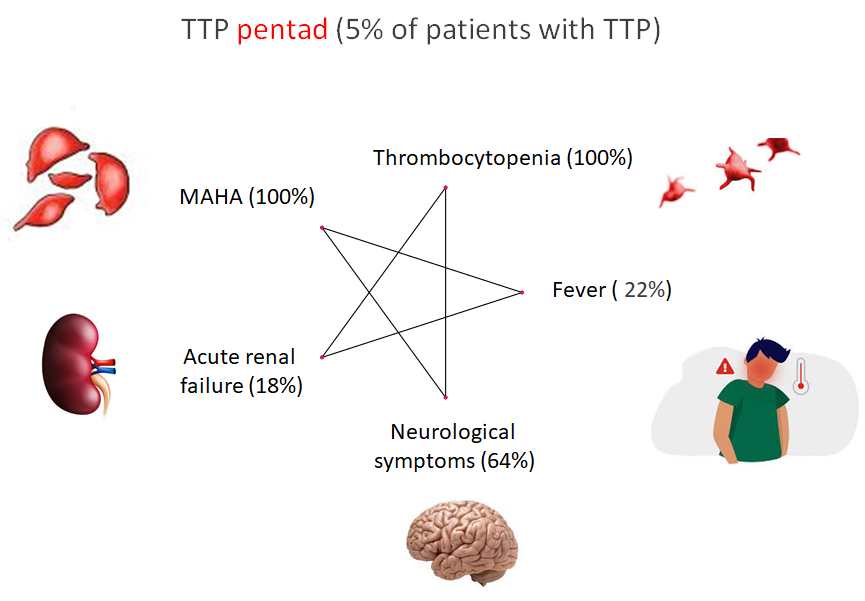
MAHA; microangiopathic hemolytic anemia; prevalence figures from J Clin Apher 2014;29:148
If ADAMTS13 activity levels are less than 10%, what is the next step?
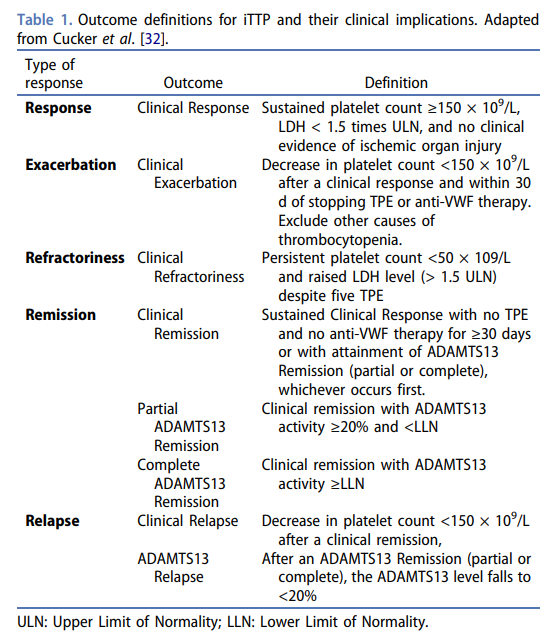
What are treatment goals in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura?
Typical sites of bleeding in ITP include:
In a patient with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in whom plasma exchange is delayed, what would you recommend?
What is Caplacizumab?
Which of the following immunosuppressant(s) should be used up front in the treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura?
True of false: red cell transfusions are relatively contraindicated in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
True of false: prophylactic platelet transfusions are relatively contraindicated in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura?
Which therapies may be instituted in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura once the platelet count > 50×109/L
It is generally safe to carry out invasive procedures on patients with platelet counts (x 109/L):
Which of the following are important to ask about in a patient with newly diagnosed thrombocytopenia?
True or false:
A diagnosis of DIC can only be made if there is a primary condition known to be associated with DIC and clinical signs and symptoms are
compatible with this underlying disease.
True of false: A single laboratory assay exists that can reliably confirm or reject a diagnosis of DIC.


True of false: disseminated intravascular coagulation is an independent (‘standalone’) clinical disorder.
In patients taking corticosteroids for immune thrombocytopenia, what should they be monitored for?
Recommended initial therapy for immune thrombocytopenia includes:
Patients with presumed immune thrombocytopenia should be tested for:
Newly diagnosed immune thrombocytopenia is ITP diagnosed within:
True of false: with the availability of the occurrence of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, there is no longer a need to obtain ADMATS13 activity levels?
Thrombocytopenia and peripheral smear showing target cells and macrocytosis suggest:
What is the estimated prevalence of thrombocytopenia (platelet count <100) in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome?
What percentage of patients with myelodysplastic syndrome present with isolated thrombocytopenia?
What is the prevalence of thrombocytopenia in alcohol-dependent patients requiring hospitalization?
In immune thrombocytopenia, at what platelet level (x 109/L) should you normally think about initiating therapy?
Chronic immune thrombocytopenia is ITP lasting:
True of false: alcohol-induced thrombocytopenia resolves with abstinence.
True of false: thrombocytopenia related to alcohol use can occur independently of liver damage.
Mechanisms of thrombocytopenia include:
Your patient with thrombocytopenia has an elevated AST and normal ALT. What are the possible explanations?
What is the prevalence of thrombocytopenia in cirrhosis?
Thrombocytopenia and peripheral smear showing schistocytes is consistent with:
How long does it take for the platelet count to recover following abstinence in a patient with alcohol-induced thrombocytopenia?
Thrombocytopenia and concomitant anemia are consistent with:
What is the prevalence of pseudothrombocytopenia in the general population?
What is the most common cause of thrombocytopenia in pregnancy?
Which statement is true:
True or false: gestational thrombocytopenia can be distinguished from immune thrombocytopenia by ordering anti-platelet antibodies.
What are the 2 main mechanisms underlying cirrhosis-associated thrombocytopenia?