Knowledge Check
Prev
1 / 0 Next
Prev
1 / 0 Next
How is macrocytosis defined?
a
Mean cell volume (MCV) > 65 fL
b
MCV > 100 fL
c
MCHC > 38 g/dL
d
MCV > 80 fL
e
RDW > 16%

Sort the condition according to the typical mean cell volume:
Iron deficiency
MDS
Hydroxyurea
Alcohol
Hb EE
Inflammation
Hyperthyroidism
Reticulocytosis
Thalassemia
Liver disease
Hb CC
Hypothyroidism
MCV < 80 fL
MCV > 100 fL
Abbreviation: MDS, myelodysplastic syndrome
True or false: increased reticulocytes cause a reduction in the mean cell volume.
a
True
b
False
They may cause an increase in the MCV.
True or false: macrocytosis may occur in the absence of anemia.
a
True
b
False
Macrocytosis without anemia is called isolated macrocytosis:
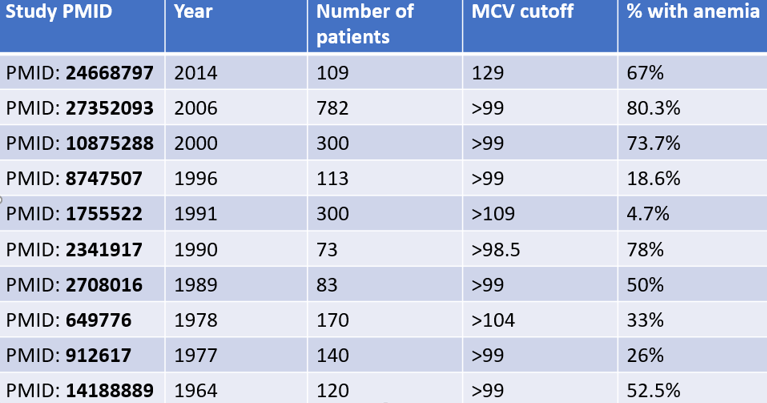

Isolated macrocytosis:
- More common in those with:
- Mean cell volume (MCV) < 110 fL
- Alcoholism
- Medication-associated macrocytosis
- Unexplained macrocytosis
- Less common in those with:
- MCV > 110 fL
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Hemolytic anemia
- Underlying none arrow disease
- Liver disease
True of false: with careful investigation, the cause of macrocytosis can be determined in virtually every patient.
a
True
b
False
A significant proportion remain undiagnosed
Prev
1 / 0 Next

