Knowledge Check
Prev
1 / 7 Next
Prev
1 / 7 Next
True of false: Smoking causes isolated elevation of neutrophils
a
True
b
False
All white blood cell subtypes are affected.
What are some proposed mechanisms of smoking-induced leukocytosis (more than one answer may apply):
a
Nicotine-associated release of catecholamines
b
Chronic systemic inflammatory response
c
Acquired Jak2 V617F mutation
d
Shortened transit time of polymorphonuclear leukocytes within the bone marrow
True or false: The effect of smoking on the white blood cell count demonstrates a dose response.
a
True
b
False
What is the mean increase in white blood cell count in smokers:
a
1%
b
10%
c
20%
d
50%
e
100%
True or false: Smoking cessation is associated with a near or complete reversal of leukocytosis.
a
True
b
False
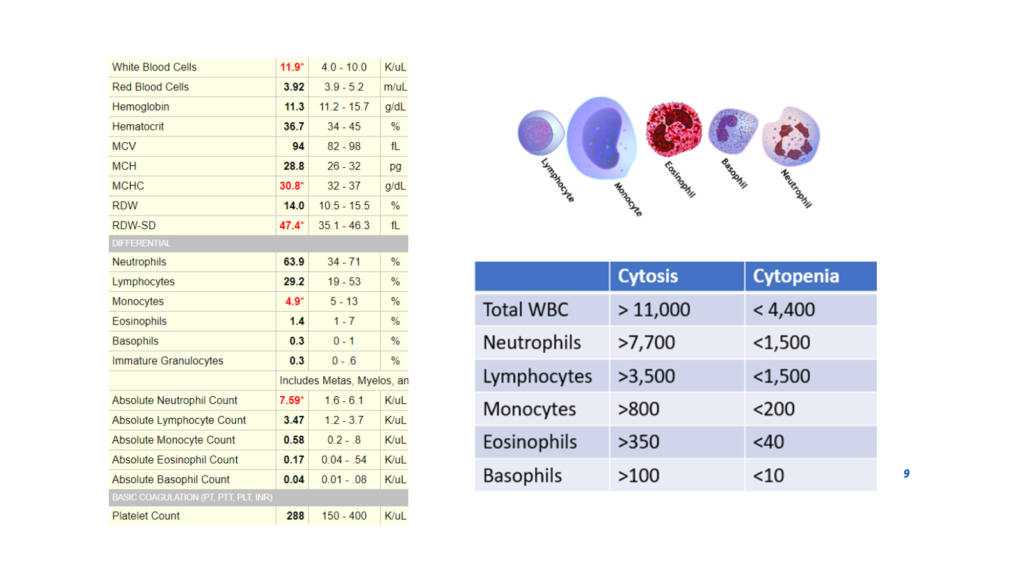
Are the above white blood cell (WBC) count and WBC differential consistent with a smoking effect?
a
Yes
This patient was indeed a smoker and there was no other obvious cause for the leukocytosis. Note that while the total white cell count meets the definition of leukocytosis, none of the individual subsets is abnormally high. Thus, the elevated white cell count represents the cumulative effect of high-normal subset counts. This is common in smokers.
b
No
Prev
1 / 7 Next

