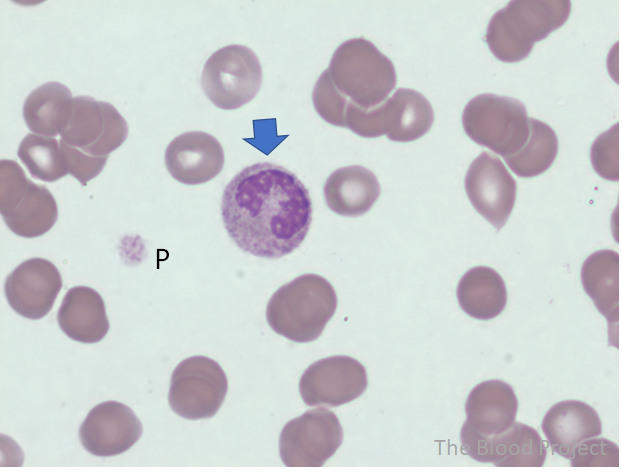
| White blood cell, neutrophil | Band neutrophil |
| Also known as | Stab cell |
| Definition | Neutrophil cytoplasm with deeply indented nucleus. The nucleus is indented to more that half the distance to the farthest nuclear margin. The nuclear shape can be variable, including U, C, S or twisted. Chromatin is consistently present between edges of nuclear membrane, but in no area is it condensed to a single filament. |
| Conditions associated with the cell type | Normally circulate (<10% of neutrophils); increased numbers in left shift (as occurs with inflammation and infection) and myeloproliferative neoplasms. Significant inter-observer variability in enumeration of band counts via a manual differential limits clinical utility. Learn more here. |
| Mechanism of formation | During maturation, the neutrophil goes through several stages, namely myeloblast, promyelocyte, myelocyte, metamyelocyte, band cell and, finally, polymorphonuclear (segmented) cell. |
| Source/author | William Aird |
| Reviewed and edited by | Parul Bhargava |
| References | Color Atlas of Hematology, CAP |