| Red blood cell, inclusion | Babesia |
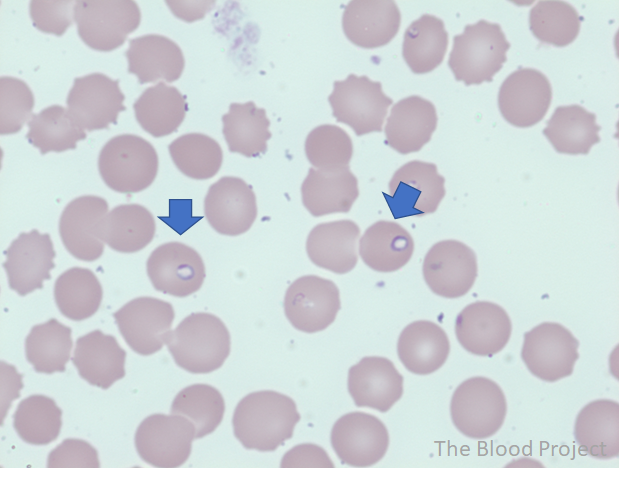
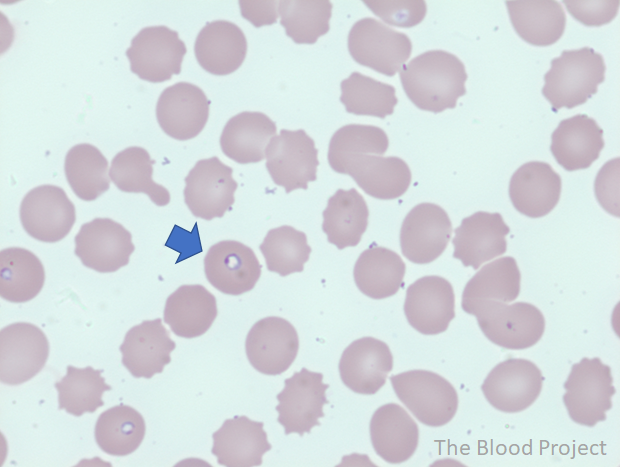
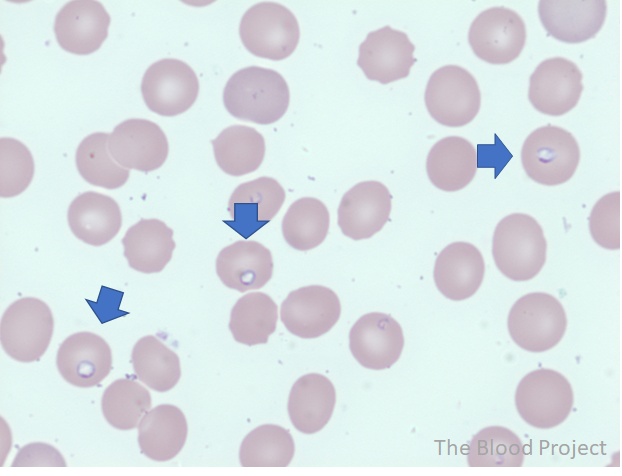
| Definition | Ring forms (trophozoites), the most common inclusion bodies in Babesiosis, are characterized by non-staining vacuole surrounded by cytoplasm (in blue) and a small nucleus (in purple). |
| Mechanism of formation | Babesia microti, an intraerythrocytic protozoan, is the main etiologic agent of human babesiosis. |
| History | First described by Viktor Babes in 1888 when he investigated the cause of hemoglobinuria in febrile cattle; first human case reported in 1957. |
| Source/author | William Aird |
| Reviewed and edited by | Parul Bhargava |
| References | Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2015;29:357 |