Agranulocytosis is a severe form of neutropenia characterized by a marked reduction or complete absence of granulocytes, especially neutrophils, in the peripheral blood.
- Definition:
- Absolute neutrophil count (ANC) < 500/μL (0.5 × 10⁹/L)
- In agranulocytosis, ANC is often < 100/μL or even zero
- Other granulocytes (eosinophils, basophils) are also typically very low or absent
- Clinical Consequences:
- Profound immunosuppression → high risk of serious, life-threatening infections
- Common manifestations:
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Oral ulcers
- Sepsis without localizing signs
- Causes:
- Drug-induced (most common)
- Clozapine, carbimazole, methimazole, PTU
- Sulfonamides, chloramphenicol, dapsone
- Chemotherapy
- Autoimmune diseases
- Lupus
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Bone marrow failure syndromes
- Aplastic anemia
- Myelodysplastic syndromes
- Infections
- EBV
- HIV
- Hepatitis
- Parvovirus
- Congenital
- Kostmann syndrome
- Drug-induced (most common)
- Pathogenesis:
- Immune-mediated
- Direct toxic mechanisms leading to destruction or suppression of neutrophil precursors
- Diagnosis:
- CBC with differential: severe neutropenia
- Bone marrow biopsy: may show granulocytic hypoplasia or aplasia
- Investigate for:
- Recent drug exposures
- Infections
- Autoimmune markers
- Treatment:
- Stop offending drug immediately (if drug-induced)
- Empiric broad-spectrum antibiotics if febrile
- Consider G-CSF (filgrastim) to speed neutrophil recovery
- Protective isolation in severe cases
- Treat underlying cause
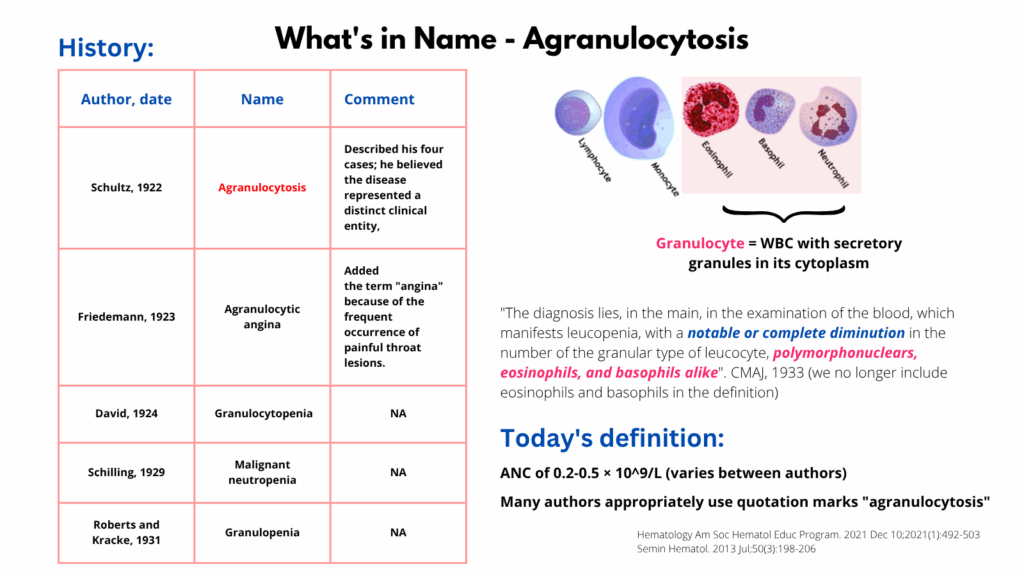
History of the term