Macrocytic Anemias
Prev
1 / 0 Next
Prev
1 / 0 Next
Macrocytic anemia
Definition
Hb < 12 g/dL (F) or < 13 g/dL (M) with mean cell volume (MCV) > 100 fL
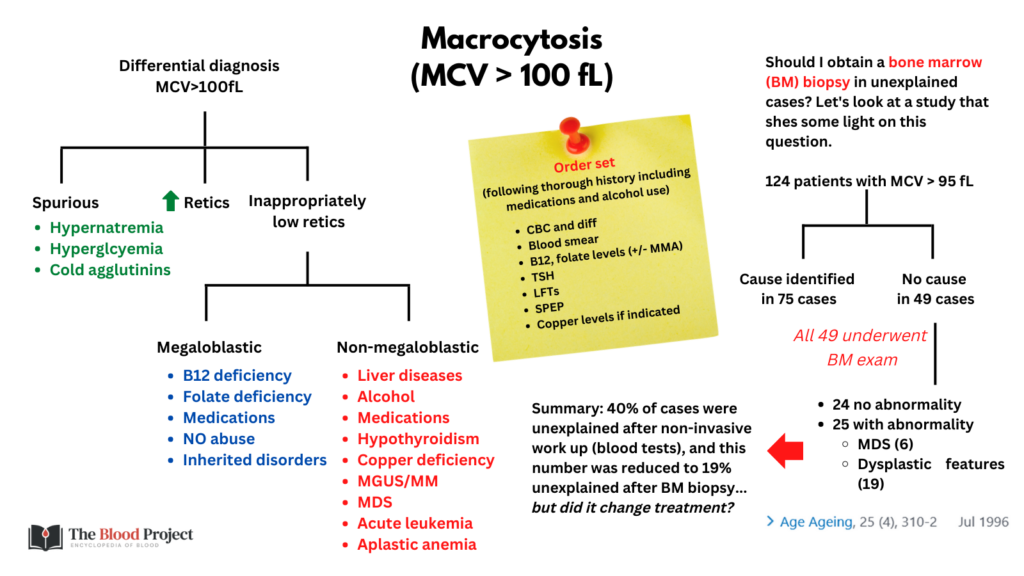
Differential diagnosis
- Most common causes of macrocytosis with or without anemia include:
- Reticulocytosis
- Cirrhosis
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Drugs
- Alcohol use
- Myelodysplastic syndrome
- Less common causes include:
- Spurious
- Aplastic anemia
- Plasma cell dyscrasia
- Hypothyroidism
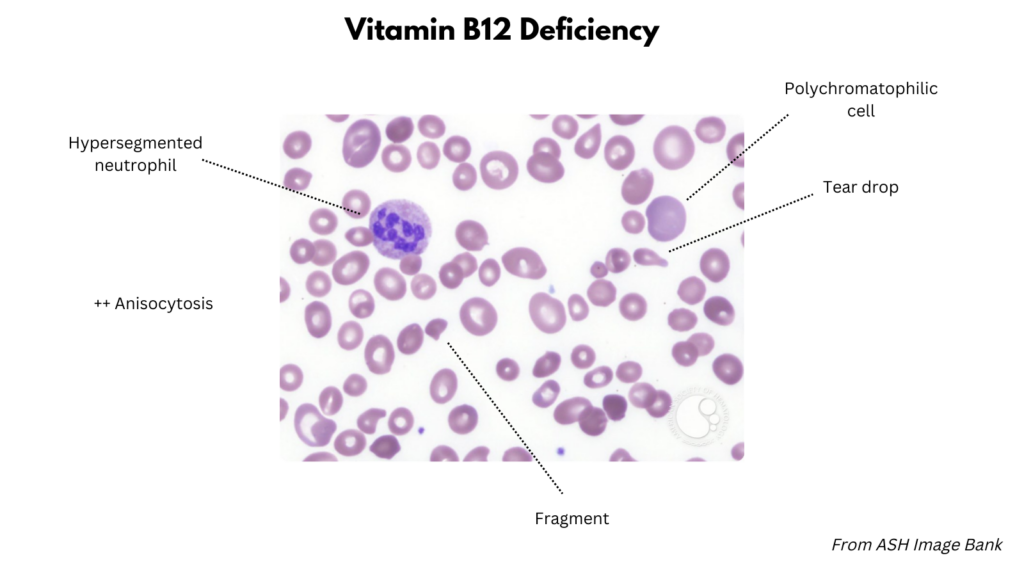
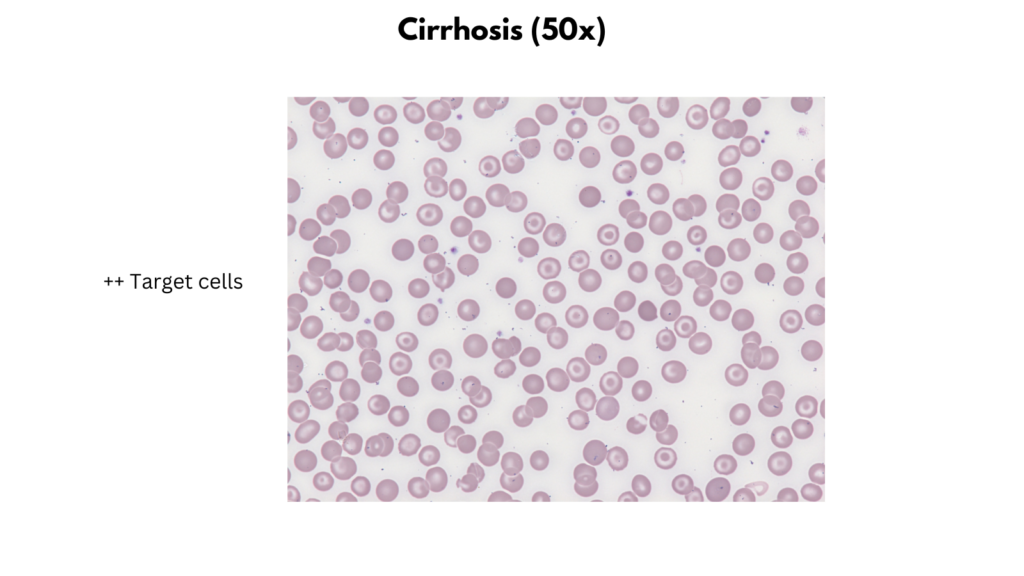
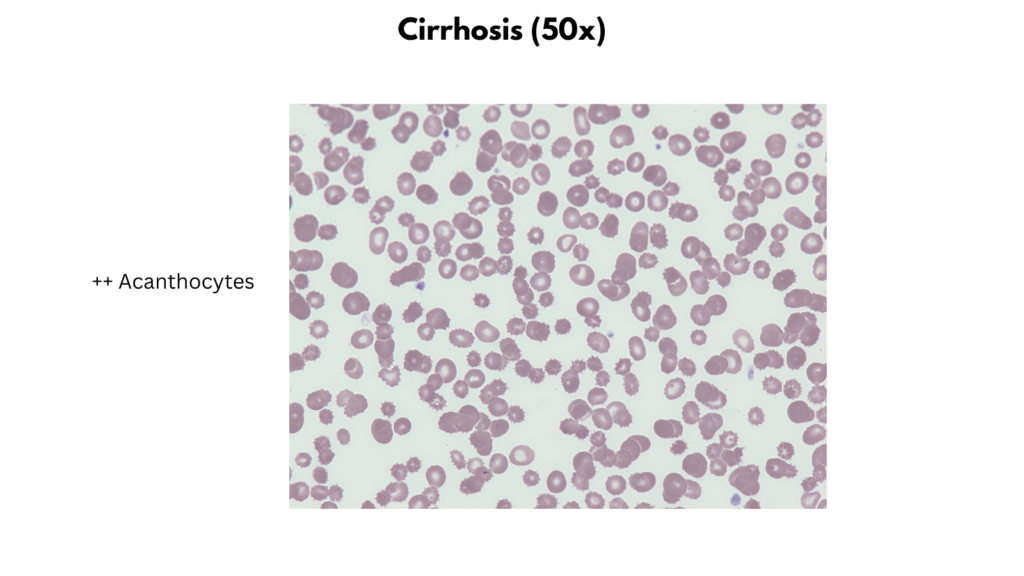
Peripheral smear findings
| Condition | Findings |
|---|---|
| Vitamin B12 deficiency | Size Macroovalocytes Anisocytosis Staining Normal central pallor Few polychromatophilic cells Shapes Fragments Inclusions Typically none Non-RBC findings Hypersegmented neutrophils Reduced platelet number |
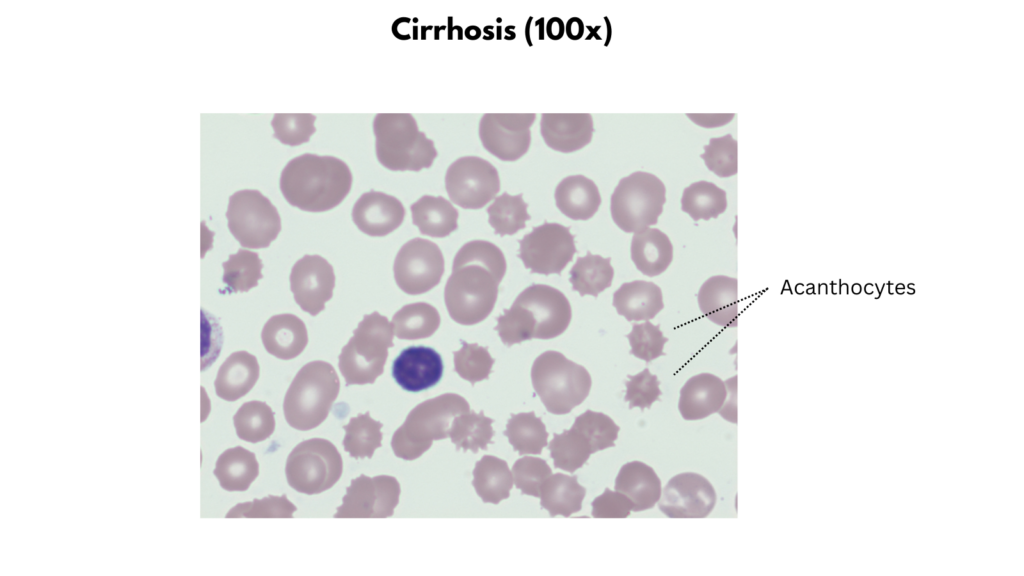
| Cirrhosis | Size Macrocytes Staining Mostly normochromic +/- Increased polychromatophilic cells Shapes Target cells Spur cells Stomatocytes (alcoholic cirrhosis) Inclusions Typically none Non-RBC findings Reduced platelet number |
Examples of peripheral smear findings
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Cirrhosis
Additional TBP resources
- Peripheral smears of:
- Physical findings in patients with macrocytic anemia
- Physical findings in patients with vitamin B12 deficiency
- Order set in macrocytic anemia
- Order set in suspected vitamin B12 deficiency
- Cirrhosis and hematology
- Graphic on spur cell vs. burr cell
- Infographic on acanthocytes
Prev
1 / 0 Next
