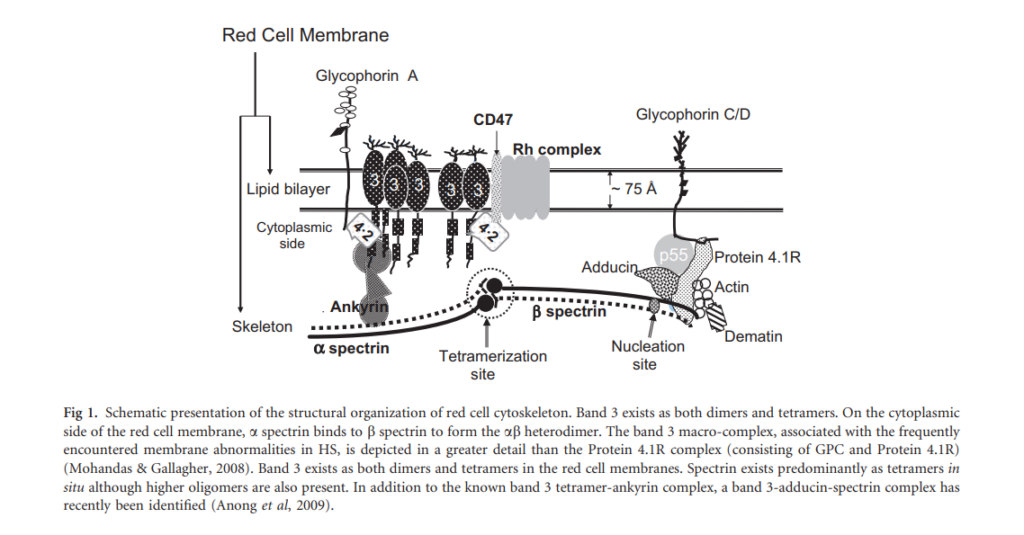
Autosomal dominant (75% of cases) or autosomal recessive (25%) mutations in genes that encode red blood cell (RBC) membrane proteins, resulting in qualitative defects of the encoded proteins. Genes with mutations include:
- ANK1 encoding ankyrin
- SLC4A1 encoding band 3
- SPTA1 encoding alpha-spectrin
- SPTB encoding beta-spectrin
- EPB42 encoding protein 4.2
Mutations results in reduced binding of spectrin cytoskeleton to lipid bilayer of RBCs, leading to reduced membrane surface area (reduced surface area-to-volume ratio), reduced RBC deformability and increased osmotic fragility.