Knowledge Check
Prev
1 / 0 Next
Prev
1 / 0 Next

Sort the conditions (top) according to the type of polycythemia/erythrocytosis (bottom):
Gaisbock’s syndrome
EPOR mutations
Chronic ling disease
Testosterone use
Renal cyst
PV
Vomiting
Diarrhea
CO poisoning
Sleep apnea
Hepatoma
Diuretics
Relative
Primary absolute
Secondary absolute
Abbreviations: PV, polycythemia vera; EPOR, erythropoietin receptor; CO, carbon monoxide
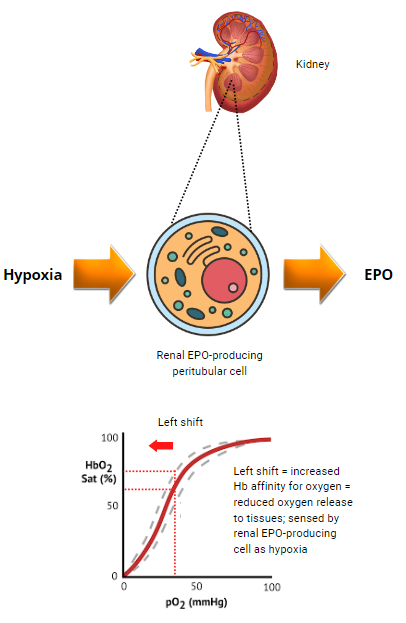
Abbreviations: ODC, oxygen dissociation curve
What tumor(s) is/are associated with secondary erythrocytosis?
a
Hepatoma
b
Atrial myxoma
c
Cerebellar hemangioblastoma
d
Uterine leiomyoma
e
Squamous cell carcinoma of skin
What is the difference between primary and secondary polycythemia/erythrocytosis?
a
Primary refers to high clinical relevance
b
Primary refers to cases occurring in childhood
c
Primary refers to cases in which the increased production of red cells is autonomous to the red cell progenitors
d
Primary refers to cases in which the increased production of red cells is driven by a factor external to the bone marrow.
Prev
1 / 0 Next

