Algorithms and Flowcharts
Prev
1 / 0 Next
Prev
1 / 0 Next
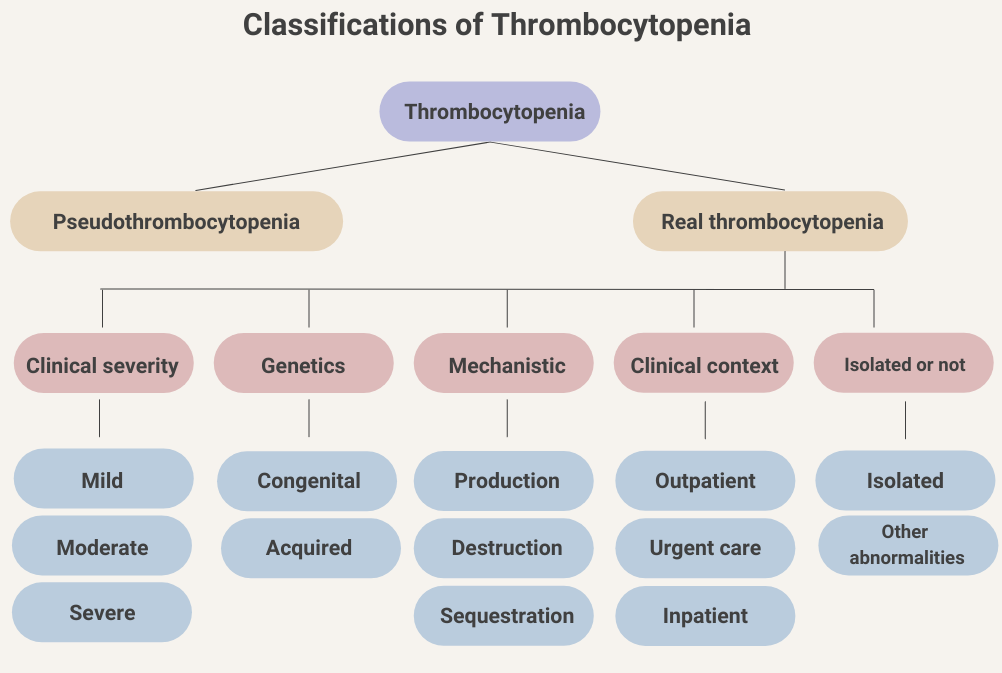
Notes:
- In a patient with new onset thrombocytopenia, rule out pseudothrombocytopenia by examining for platelet clumping on a peripheral smear.
- See next slide for more information about classification according to clinical context.
- Isolated thrombocytopenia refers to thrombocytopenia in the absence of other abnormalities in the complete blood count.
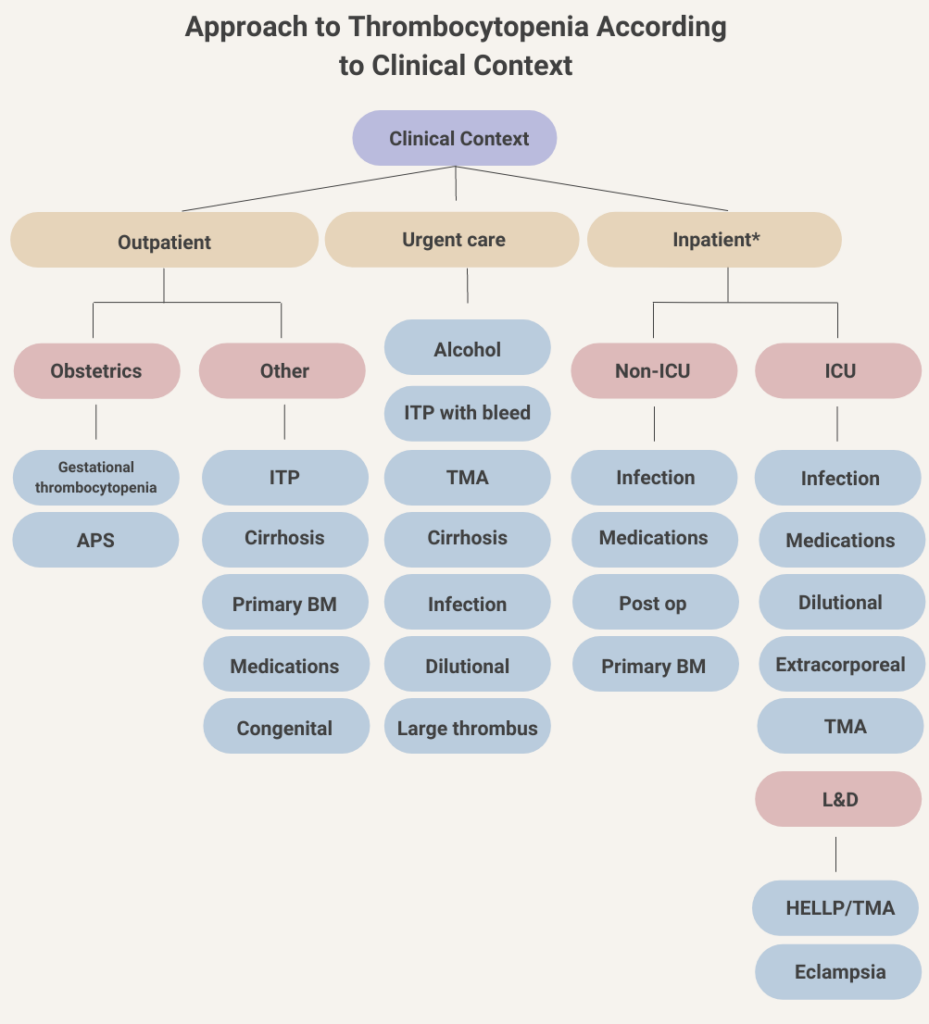
Notes:
- Alcohol toxicity is one of the most common causes of thrombocytopenia in the Emergency Department.
- Dilutional thrombocytopenia may develop in a patient receiving massive red cell transfusion without appropriate platelet transfusion support. This may develop in a trauma patient presenting to the Emergency Department, in a patient undergoing surgery or an invasive procedure, or in an obstetrical patient with postpartum hemorrhage.
- Patients with a high clot burden (“large thrombus”) may develop thrombocytopenia from consumption of platelets in the thrombus. They may present to the Emergency Department or they may develop de novo thrombosis in the hospital.
Prev
1 / 0 Next
