Outcomes
Prev
1 / 0 Next
Prev
1 / 0 Next

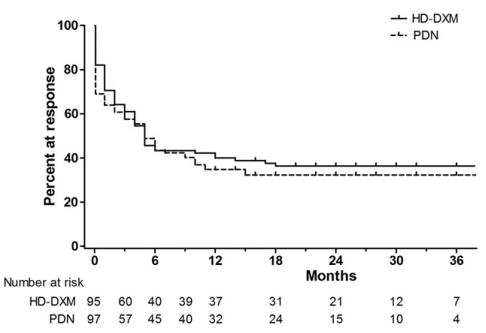
Comparisons are high-dose dexamethasone vs. prednisone:
Primary Outcomes:
- OR, n (%): 78 (82.1) vs. 67 (69.1), P=0.044 (dexamethasone superior)
- SR, n (%): 38 (40.0) vs. 40 (41.2), P= 0.884
Secondary Outcomes:
- Efficacy
- CR, n (%): 48 (50.5) vs. 26 (26.8), P=0.001 (dexamethasone superior)
- Sustained CR, n (%): 26 (27.4) vs. 17 (17.5), P=0.120
- Median time to response (TTR), d (range): 3 (1-9) vs. 6 (2-24), P=0.001 (dexamethasone superior)
- Bleeding events: 12 vs. 25, P=0.028 (dexamethasone superior)
- Safety
- Both treatments were well-tolerated in general. The frequency of adverse events was higher in the prednisone arm, especially with cushingoid appearance and weight gain in > 10% of the patients. Several other adverse events were observed in > 5% of patients in each arm, including insomnia and mood disorders in the high-dose dexamethasone arm and dizziness, hyperglycemia, hypertension, insomnia, and peptic ulcer disease in the prednisone arm.

Prev
1 / 0 Next
