Labs
Let’s begin with the patient’s CBC at the time of admission:
| WBC (109/L) | Hb (g/dL) | MCV (fL) | PLT (109/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4.9 | 11.1 | 91 | 343 |
What’s what: WBC, white blood cell count; Hb, hemoglobin; MCV, mean cell volume; MCHC, mean cellular hemoglobin concentration; RDW-SD, red cell distribution width-standard deviation; platelets, PLT; Normal values: WBC 5-10 x 109/L, RBC 4-6 x 1012/L, Hb 12-16 g/dL, Hct 35-47%, MCV 80-100 fL, MCHC 32-36 g/dL, RDW-SD < 45 fL, platelets (PLT) 150-450 x 109/L
Now let’s jump to day 13 postop when you first see her:
| WBC (109/L) | Hb (g/dL) | MCV (fL) | PLT (109/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10.7 | 8.6 | 88 | 1006 |
What’s what: WBC, white blood cell count; Hb, hemoglobin; MCV, mean cell volume; MCHC, mean cellular hemoglobin concentration; RDW-SD, red cell distribution width-standard deviation; platelets, PLT; Normal values: WBC 5-10 x 109/L, RBC 4-6 x 1012/L, Hb 12-16 g/dL, Hct 35-47%, MCV 80-100 fL, MCHC 32-36 g/dL, RDW-SD < 45%, platelets (PLT) 150-450 x 109/L
So, the patient has new-onset thrombocytosis occurring in the postop setting.
Trends (time series) in lab values often tell important stories!
… so let’s look at the platelet count trend from day of admission to postop day 13, when you first see her.
The platelet count trend is as follows:
| Hospital day relative to surgery | Platelet Count (x 109/L) |
|---|---|
| D13 | 1006 |
| D12 | 915 |
| D11 | 861 |
| D10 | 815 |
| D9 | 697 |
| D8 | 534 |
| D7* | 492 |
| D4 | 271 |
| D3 | 195 |
| D2 | 187 |
| D1 | 182 |
| D0 (day of admission) | 343 |
*No CBC was obtained between postop days 4 and 7
We see an initial drop in the platelet count, which is typical for patients undergoing cardiothoracic surgery, followed by a progressive increase towards 1000 x 109/L.
What would you look for in the white cell count and Hb?
We have already established that the thrombocytosis is new, occurring in the post op setting. The platelet count trend is as follows:
| Hospital day relative to surgery | Platelet Count (x 109/L) |
|---|---|
| D13 | 1006 |
| D12 | 915 |
| D11 | 861 |
| D10 | 815 |
| D9 | 697 |
| D8 | 534 |
| D7* | 492 |
| D4 | 271 |
| D3 | 195 |
| D2 | 187 |
| D1 | 182 |
| D0 (day of admission) | 343 |
*No CBC was obtained between days 4 and 7
We see an initial drop in the platelet count, which is typical for patients undergoing cardiothoracic surgery, followed by a progressive increase towards 1000 x 109/L.
What would you look for in the white cell count and Hb?
- An increasing white cell count might suggest postoperative infection, which may, in turn, be associated with secondary (reactive) thrombocytosis.
- A significant drop in Hb might suggest blood loss, which may, in turn, be associated with secondary (reactive) thrombocytosis.
The corresponding white cell count and Hb values are as follows:
| Hospital day relative to surgery | WBC (x 109/L) | Hb (g/dL) | Platelet Count (x 109/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| D13 | 10.7 | 8.6 | 1006 |
| D12 | 14.1 | 9.5 | 915 |
| D11 | 13.2 | 8.9 | 861 |
| D10 | 13 | 9.5 | 815 |
| D9 | 11.7 | 9.2 | 697 |
| D8 | 10.4 | 8.9 | 534 |
| D7* | 11.2 | 9.0 | 492 |
| D4 | 11 | 9.7 | 271 |
| D3 | 13.2 | 8.4 | 195 |
| D2 | 15.7 | 9.0 | 187 |
| D1 | 12.6 | 8.7 | 182 |
| D0 (day of admission) | 4.9 | 11.1 | 343 |
What’s what: WBC, white blood cell count; Hb, hemoglobin; MCV, mean cell volume; MCHC, mean cellular hemoglobin concentration; RDW-SD, red cell distribution width-standard deviation; platelets, PLT; Normal values: WBC 5-10 x 109/L, RBC 4-6 x 1012/L, Hb 12-16 g/dL, Hct 35-47%, MCV 80-100 fL, MCHC 32-36 g/dL, RDW-SD < 45 fL, platelets (PLT) 150-450 x 109/L
The corresponding white cell count and Hb values are as follows:
| Hospital day relative to surgery | WBC | Hb | Platelet Count |
|---|---|---|---|
| D13 | 10.7 | 8.6 | 1006 |
| D12 | 14.1 | 9.5 | 915 |
| D11 | 13.2 | 8.9 | 861 |
| D10 | 13 | 9.5 | 815 |
| D9 | 11.7 | 9.2 | 697 |
| D8 | 10.4 | 8.9 | 534 |
| D7* | 11.2 | 9.0 | 492 |
| D4 | 11 | 9.7 | 271 |
| D3 | 13.2 | 8.4 | 195 |
| D2 | 15.7 | 9.0 | 187 |
| D1 | 12.6 | 8.7 | 182 |
| D0 (day of admission) | 4.9 | 11.1 | 343 |
What’s what: WBC, white blood cell count; Hb, hemoglobin; MCV, mean cell volume; MCHC, mean cellular hemoglobin concentration; RDW-SD, red cell distribution width-standard deviation; platelets, PLT; Normal values: WBC 5-10 x 109/L, RBC 4-6 x 1012/L, Hb 12-16 g/dL, Hct 35-47%, MCV 80-100 fL, MCHC 32-36 g/dL, RDW-SD < 45 fL, platelets (PLT) 150-450 x 109/L
The patient has leukocytosis and anemia, though neither is progressive, and both are consistent with a postoperative effect. The WBC differential would be helpful, since a left shift might point towards an infectious process.
For fun, let’s determine the patient’s “platelet-crit” (the fractional volume of blood that is composed of platelets). We know the platelet count is 1006 x 109/L. What additional value do we need to calculate the platelet-crit?
Mean platelet volume is about 9 fL.
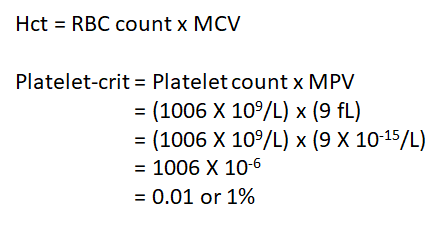

The normal range for the platelet-crit (PCT) is 0.22–0.24%.
When you see the patient, she is 13 days post op. The following history provides more information about her course in hospital before you see her:
The patient was admitted to the ICU following surgery in stable condition. She received venous thromboembolism (VTE) prophylaxis and an H2 blocker for GI prophylaxis. She was restarted on her pre-op aspirin and statin. On post op day 2, she developed hypoxia, and was started on Lasix. On post op day 4, her platelet counts started to increase. Chest tubes were removed. On post op day 7, she developed increasing shortness of breath. CXR revealed a new moderate left pleural effusion. On postop day 8, she developed a small mount of serous draining from the sternum. On postop day 9, her pleural effusion persisted despite aggressive diuresis. She remained clinically stable between postop days 10 and 12. On postop day 13, the day you see her (with a platelet count of 1006 x 109/L), her sternal wound is noted to have superficial dehiscence and purulent drainage. She is started on vancomycin and cefazolin, and the wound is debrided.
What is/are the most likely cause(s) of the patient’s thrombocytosis?

